Dessinez les structures des éthers suivants :
| 1) Éther butyléthylique 2) Ethyl phényl éther 3) Éther diphénylique 4) Éther divinylique 5) Isopropoxybutane 6) Benzyl phényl éther 7) Méthoxycyclohexane 8) 4-méthoxypent-2-ène 9) 4-éthoxybut-1-yne 10) Cyclohexyl phényl éther |
11) 2-Chlorophényl phényl éther 12) éther isopropylique de tert-butyle 13) 2-Méthoxy-3-phénylbutan-1-ol 14) Éther diéthylique 15) m-éthoxyphénol 16) 2,3-diméthyloxacyclopropane 17) 3-Méthoxyoxacyclohexane 18) 2-éthyl-3-méthyloxacyclopentane 19) Éther de cyclohexyle et de cyclopropyle 20) 2-Méthoxypentane |
SOLUTION:
1) Éther butyléthylique
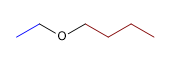
2) Ethyl phényl éther
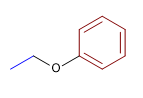
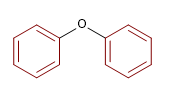
3) Éther diphénylique
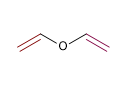
4) Éther divinylique
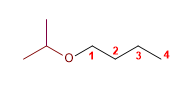
5) Isopropoxybutane
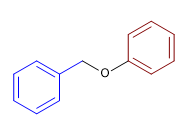
6) Benzyl phényl éther
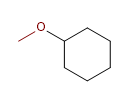
7) Méthoxycyclohexane
8) 4-méthoxypent-2-ène
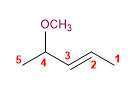
9) 4-éthoxybut-1-yne
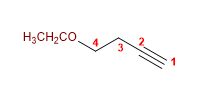
10) Cyclohexyl phényl éther
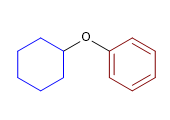
![]() Les groupements alcoxydes (méthoxyde, éthoxyde...) sont classés par ordre alphabétique avec les autres substituants de la molécule et n'ont aucune préférence sur eux
Les groupements alcoxydes (méthoxyde, éthoxyde...) sont classés par ordre alphabétique avec les autres substituants de la molécule et n'ont aucune préférence sur eux
.
11) 2-Chlorophényl phényl éther
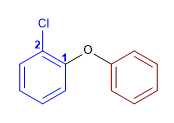
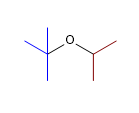
12) éther isopropylique de tert-butyle
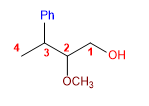
13) 2-Méthoxy-3-phénylbutan-1-ol
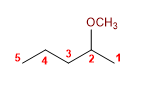
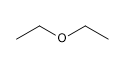
14) Éther diéthylique
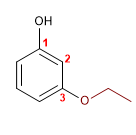
15) m-éthoxyphénol
16) 2,3-diméthyloxacyclopropane
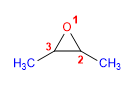
17) 3-Méthoxyoxacyclohexane
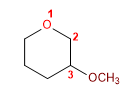
18) 2-éthyl-3-méthyloxacyclopentane
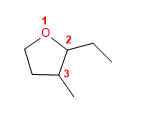
19) Éther de cyclohexyle et de cyclopropyle
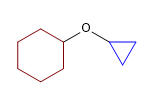
20) 2-Méthoxypentane