Nommez les éthers suivants :
SOLUTION:
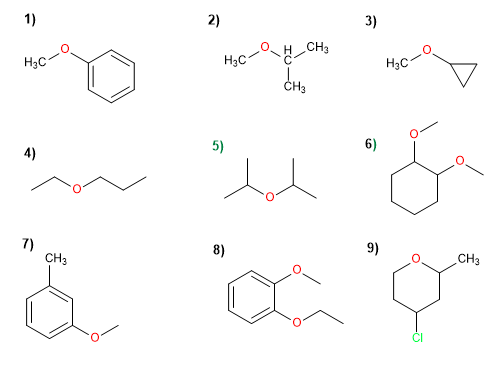
Molécule 1.
1. Substituants : phényle et méthyle
2. Nom : Phényl méthyl éther
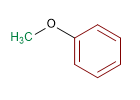
Molécule 2.
1. Substituants : isopropyle et méthyle
2. Nom : Éther isopropylméthylique
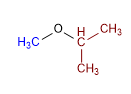
Molécule 3.
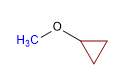
1. Substituants : cyclopropyle et méthyle
2. Nom : Cyclopropyl méthyl éther
![]() Le nom des éthers est construit en terminant par le mot éther le nom des chaînes qui partent de l'oxygène. Ces chaînes sont nommées en tant que substituants et sont classées par ordre alphabétique. Notez l'espace entre les mots.
Le nom des éthers est construit en terminant par le mot éther le nom des chaînes qui partent de l'oxygène. Ces chaînes sont nommées en tant que substituants et sont classées par ordre alphabétique. Notez l'espace entre les mots.
Molécule 4.
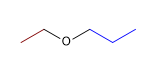
1. Substituants : éthyle et propyle
2. Nom : éther éthylique de propyle
Molécule 5.
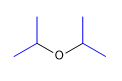
1. Substituants : isopropyles
2. Nom : éther diisopropylique
Molécule 6.
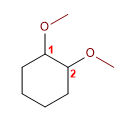
1. Chaîne principale : cycle à six chaînons (cyclohexane)
2. Numérotation : Donner des locants inférieurs aux substituants
3. Substituants : 1,2- méthylates
4. Nom : 1,2 -Di méthoxy cyclohexane
Molécule 7.
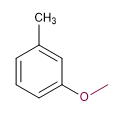
1. Chaîne principale : Toluène
2. Numérotation : méthyle et méta-méthylate.
3. Substituants : méthylate
4. Nom : m - méthoxy toluène
Molécule 8.
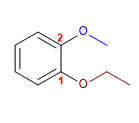
1. Chaîne principale : Benzène
2. Numérotation : Commence à l'éthoxy (précédemment par ordre alphabétique)
3. Substituants : 1 - éthoxyde et 2 - méthoxyde . (position de but)
4. Nom : m - Ethoxy méthoxy benzène
Molécule 9.
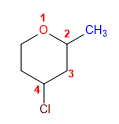
1. Chaîne principale : cycle à 6 chaînons (oxacyclohexane)
2. Numérotation : Commencer à l'oxygène, continuer vers la droite pour donner aux substituants les locants mineurs.
3. Substituants : chlore et méthyle
4. Nom : 4 - Chloro - 2 - méthyl oxa cyclohexane