Zeichnen Sie die Strukturen der folgenden Äther:
| 1) Butylethylether 2) Ethylphenylether 3) Diphenylether 4) Divinylether 5) Isopropoxybutan 6) Benzylphenylether 7) Methoxycyclohexan 8) 4-Methoxypent-2-en 9) 4-Ethoxybut-1-in 10) Cyclohexylphenylether | 11) 2-Chlorphenylphenylether 12) tert-Butylisopropylether 13) 2-Methoxy-3-phenylbutan-1-ol 14) Diethylether 15) m-Ethoxyphenol 16) 2,3-Dimethyloxacyclopropan 17) 3-Methoxyoxacyclohexan 18) 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxacyclopentan 19) Cyclohexylcyclopropylether 20) 2-Methoxypentan |
LÖSUNG:
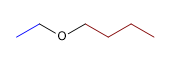
1) Butylethylether
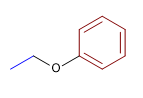
2) Ethylphenylether
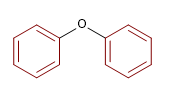
3) Diphenylether
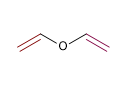
4) Divinylether
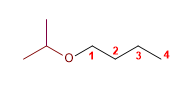
5) Isopropoxybutan
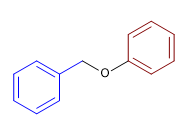
6) Benzylphenylether
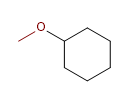
7) Methoxycyclohexan
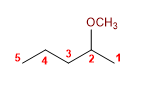
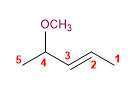
8) 4-Methoxypent-2-en
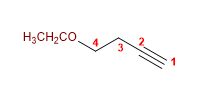
9) 4-Ethoxybut-1-in
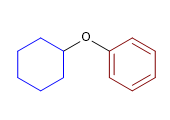
10) Cyclohexylphenylether
![]() Die Alkoholatgruppen (Methylat, Ethoxid...) sind mit den anderen Substituenten des Moleküls alphabetisch geordnet und haben gegenüber diesen keine Bevorzugung
Die Alkoholatgruppen (Methylat, Ethoxid...) sind mit den anderen Substituenten des Moleküls alphabetisch geordnet und haben gegenüber diesen keine Bevorzugung
.
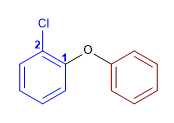
11) 2-Chlorphenylphenylether
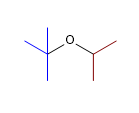
12) tert-Butylisopropylether
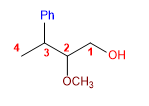
13) 2-Methoxy-3-phenylbutan-1-ol
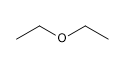
14) Diethylether
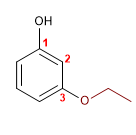
15) m-Ethoxyphenol
16) 2,3-Dimethyloxacyclopropan
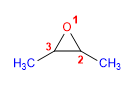
17) 3-Methoxyoxacyclohexan
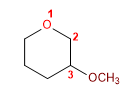
18) 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxacyclopentan
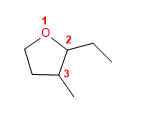
19) Cyclohexylcyclopropylether
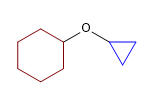
20) 2-Methoxypentan