Nennen Sie die folgenden Moleküle, in denen die Estergruppe als Substituent fungiert
LÖSUNG:
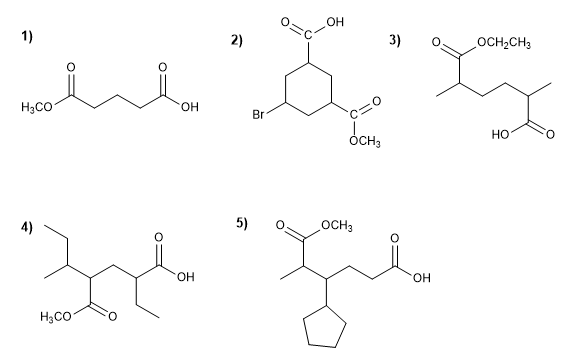
Molekül 1.
1. Hauptfunktion: Carbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Methoxycarbonyl) in 4
4. Name: 4-Methoxycarbonylbuttersäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Methoxycarbonyl) in 4
4. Name: 4-Methoxycarbonylbuttersäure
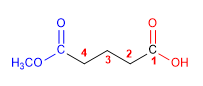
Molekül 2.
1. Hauptfunktion: Carbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit kleinem Lokant (unnummerierter Kohlenstoff)
3. Substituenten: 3-Brom- und 5-(Methoxycarbonyl)ester
4. Name: 3-Brom-5-methoxycarbonylcyclohexancarbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit kleinem Lokant (unnummerierter Kohlenstoff)
3. Substituenten: 3-Brom- und 5-(Methoxycarbonyl)ester
4. Name: 3-Brom-5-methoxycarbonylcyclohexancarbonsäure
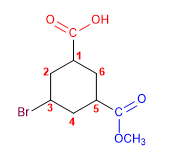
Molekül 3.
1. Hauptfunktion: Carbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Ethoxycarbonyl) in 5
4. Name: 5-Ethoxycarbonylhexansäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Ethoxycarbonyl) in 5
4. Name: 5-Ethoxycarbonylhexansäure
Molekül 4.
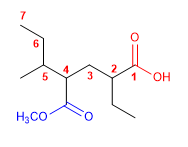
1. Hauptfunktion: Carbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Methoxycarbonyl) bei 4, Ethyl bei 2 und Methyl bei 5
4. Name: 2-Ethyl-5-methyl-4-methoxycarbonylheptansäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: Ester (Methoxycarbonyl) bei 4, Ethyl bei 2 und Methyl bei 5
4. Name: 2-Ethyl-5-methyl-4-methoxycarbonylheptansäure
Molekül 5.
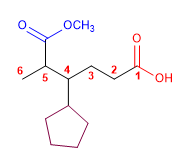
1. Hauptfunktion: Carbonsäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: 5-(Methoxycarbonyl)ester, 4-Cyclopentyl
4. Bezeichnung: 4-Cyclopentyl-5-methoxycarbonylhexansäure
2. Nummerierung: g. funktionsfähig mit Minor Locator
3. Substituenten: 5-(Methoxycarbonyl)ester, 4-Cyclopentyl
4. Bezeichnung: 4-Cyclopentyl-5-methoxycarbonylhexansäure