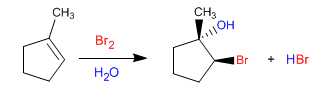
Alkenes react with halogens in an aqueous medium to form halohydrins, compounds that contain a halogen and a hydroxyl group in neighboring positions.
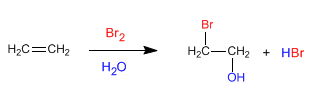
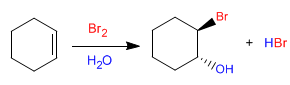
The bromohydrin formed is ANTI. The bromine and the hydroxyl group are on opposite sides as can be seen in the following example.
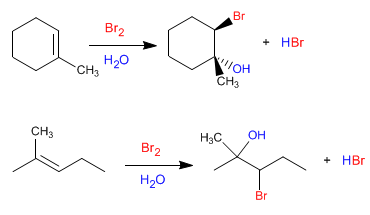
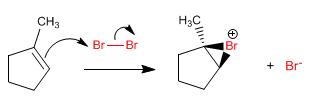
The reaction is regioselective, adding the hydroxyl group to the most substituted carbon of the alkene and the least halogen. This regioselectivity can be easily understood by looking at the mechanism.
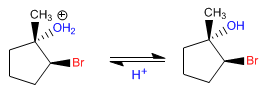
The mechanism consists in the formation of a halonium ion that is opened by water attack on the most substituted carbon.
Let the overall reaction be:
Stage 1. Bromination of the halonium ion by addition of the bromine to the alkene.
Stage 2. Opening of the bromonium ion by attack of water on the most substituted carbon
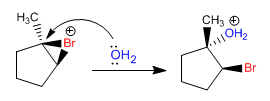
Stage 3. Deprotonation