The characteristic reaction of alkenes is the addition of substances to the double bond, according to the equation: 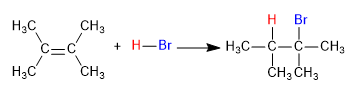
The first stage of the reaction is the addition of the proton to the nucleophilic alkene, to form the carbocation. In the second stage, the carbocation reacts with the nucleophile. 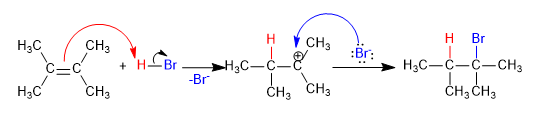
The addition of electrophiles to alkenes makes possible the synthesis of many classes of compounds: 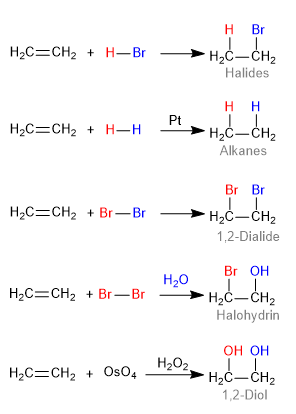
Alkyl halides, alcohols, alkanes, diols, ethers can be synthesized from alkenes by electrophilic substitution reactions. The product obtained depends only on the electrophile and the nucleophile used in the reaction.