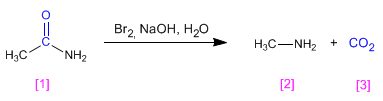AMIDES THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 115178
Amides are named as derivatives of carboxylic acids by substituting the -oic ending of the acid for -amide .
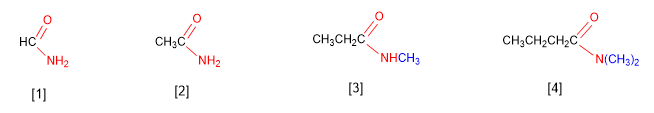
[1] Methanamide
[2] Ethanamide
[3] N-Methylpropanamide
[3] N,N-Dimethylbutanamide
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 83341
a) Amides can be obtained by reacting amines with alkanoyl halides and anhydrides .
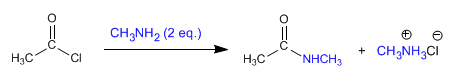
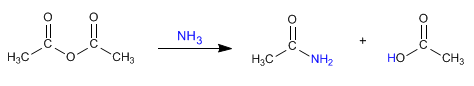
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 50306
Lactams are cyclic amides obtained by condensation, with loss of water, of a molecule containing acid and amino groups. 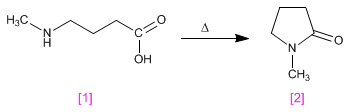
4-(aminomethyl)butanoic acid [1] condenses under heating to form N-methylpyrrolidin-2-one [2] , a polar aprotic solvent.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 45129
Imides are compounds that contain two acyl groups attached to a nitrogen by single bonds. Succinimide and Phthalimide are well known. 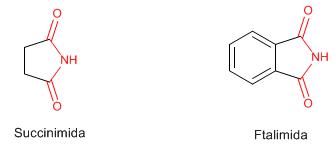
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 61464
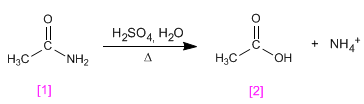
Ethanamide hydrolyzes in a sulfuric medium to form ethanoic acid .
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 53853
The amides are transformed into amines and carboxylic acids by treatment with aqueous soda under heating.
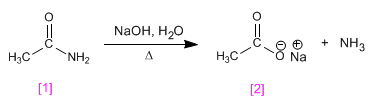
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 25329
The amides have acidic hydrogens of Pka = 15 on the nitrogen atom. Deprotonation of the amino generates a resonance stabilized base, called amidate.
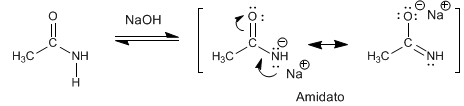
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 20198
The amides present acidic hydrogens of Pka = 30 on the carbon a . Deprotonation of the a position generates a resonance stabilized base, called the amide enolate.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 32823
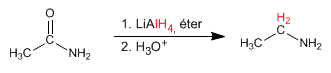
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 27496
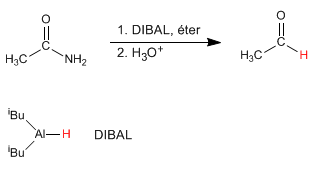
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMIDES THEORY
- Hits: 48551
Amides are transformed into amines with one less carbon, when treated with bromine in basic solution.