THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 38002
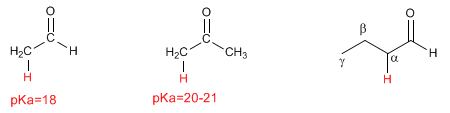
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 31969
Enolates act as nucleophiles through carbon, attacking a large number of electrophiles (haloalkanes, epoxides, carbonyls, esters...). At this point we will focus on the reaction between enlolates and haloalkanes, which allows the addition of carbon chains to the a position of the chain.
Cyclohexanone is converted to 2-Methylcyclohexanone by treatment with LDA followed by methyl iodide. 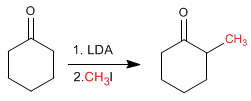
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 21553
Aldehydes and ketones exchange their hydrogens for deuteriums when treated with DO- /D2O or with D+ /D2O. In basic media the reaction proceeds through enolates and in acidic media the intermediates formed are enols. 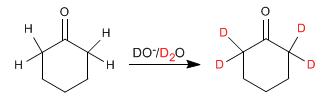
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 54910
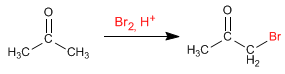
Halogenation of propanone in an acid medium:
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 104354
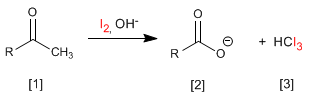
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 109926
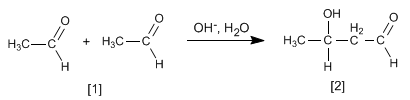
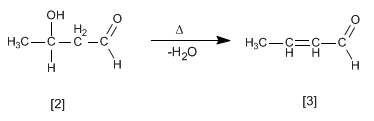
The aldol formed dehydrates in the basic medium by heating to form an a , b -unsaturated.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 49973
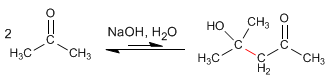
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 45288
Thus, 2,6-heptanedione condenses with methoxide in methanol to form 3-methylcyclohex-2-enone.
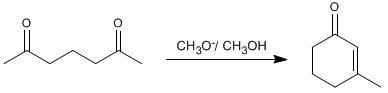
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 74876
The reaction between two different carbonyls is called crossed or mixed aldol. This reaction only has synthetic utility in two cases:
1. Only one of the carbonyls can form enolates.
2. One of the carbonyls is much more reactive than the other.
In all other situations, the mixed aldol generates mixtures of four products. Let's see as an example the condensation of ethanal and propanal. 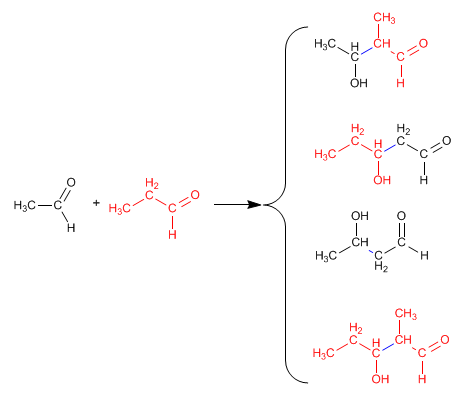
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 65486
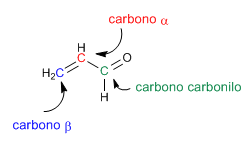 The a,b -unsaturated carbonyls are organic compounds that have a double bond between the a,b positions of an aldehyde or ketone.
The a,b -unsaturated carbonyls are organic compounds that have a double bond between the a,b positions of an aldehyde or ketone.
Propenal or acrolein is an a,b -unsaturated carbonyl. Its two conjugated double bonds give it special reactivity.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 50108
The a,b -unsaturated are compounds that have two electrophilic positions: the carbonyl carbon and the b carbon.
Additions 1,2. Lithium organometallics attack the carbonyl carbon giving rise to 1,2 additions. 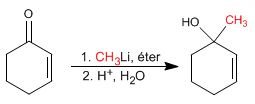
![]() The organometallics of lithium and magnesium attack the carbonyl carbon of the a,b-unsaturates
The organometallics of lithium and magnesium attack the carbonyl carbon of the a,b-unsaturates
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY OF ENOLS AND ENOLATES
- Hits: 52282
Enolates of aldehydes or ketones add to the a,b-unsaturated to form 1,5-dicarbonyls. This reaction is called the Michael addition. 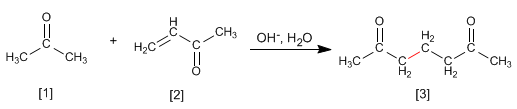
Propanone reacts with a,b-unsaturated to form 1,5-dicarbonyl