Name the following cycloalkenes: 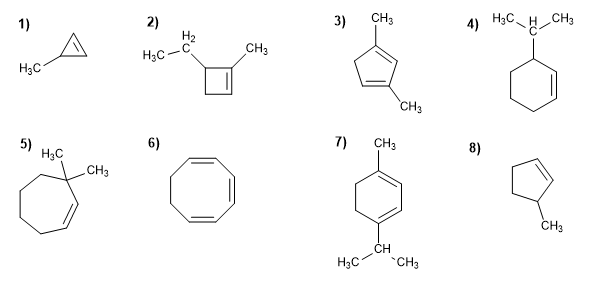
SOLUTION:
Molecule 1.
1. Main chain: 3-membered cycle (cyclopropene)
2. Numbering: the double bond takes the minor locants
3. Substituents: methyl in position 3
4. Name: 3-Methylcyclopropene
![]() In cyclic molecules, the double bond will always occupy position 1 and this locant can be omitted when naming the alkene (this is true in the absence of functional groups).
In cyclic molecules, the double bond will always occupy position 1 and this locant can be omitted when naming the alkene (this is true in the absence of functional groups).
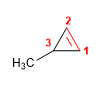
Molecule 2.
1. Main chain: 4-membered cycle (cyclobutene)
2. Numbering: numbering begins at the methyl carbon so that the double bond and the substituents take the lowest locants.
3. Substituents: methyl in position 1 and ethyl in 4
4. Name: 4-Ethyl-1-methylcyclobutene
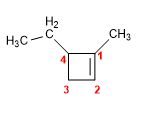
Molecule 3.
1. Main chain: 5-membered cycle (cyclopentadiene)
2. Numbering: lowest possible locants to double bonds and methyls.
3. Substituents: methyls in position 1,3 .
4. Name: 1,3-Dimethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene
Molecule 4.
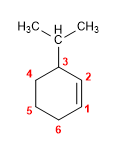
1. Main chain: 6-membered cycle (cyclohexene)
2. Numbering: we number from the double bond, so that the isopropyl takes the lowest locant.
3. Substituents: isopropyl in position 3 .
4. Name: 3-Isopropylcyclohexene
Molecule 5.
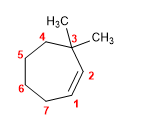
1. Main chain: 7-membered cycle (cycloheptene)
2. Numbering: we number from the double bond, so that the methyls take the lowest possible locant.
3. Substituents: methyls in position 3,3 .
4. Name: 3,3-Dimethylcycloheptene
Molecule 6.
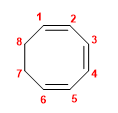
1. Main chain: 8-membered cycle (cyclooctatriene)
2. Numbering: lowest possible locants to double bonds.
3. Substituents: none.
4. Name: Cycloocta-1,3,5-triene
Molecule 7.
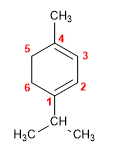
1. Main chain: 6-membered cycle (cyclohexene)
2. Numbering: locant 1 to the isopropyl double bond since it comes first in alphabetical order.
3. Substituents: 1-position isopropyl and 3-position methyl.
4. Name: 1-Isopropyl-4-methylcyclohexa-1,3-diene
Molecule 8.
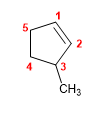
1. Main chain: 5-membered cycle (cyclopentene)
2. Numbering: we number from the double bond so that methyl takes the lowest locant.
3. Substituents: methyl in position 3 .
4. Name: 3-Methylcyclopentene