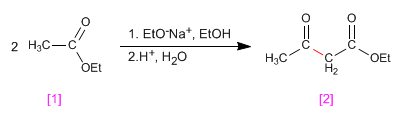ESTERS THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 212578
Esters come from condensing acids with alcohols and are named as salts of the acid from which they come. IUPAC nomenclature changes the -oic ending of the acid to -oate , ending with the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen.
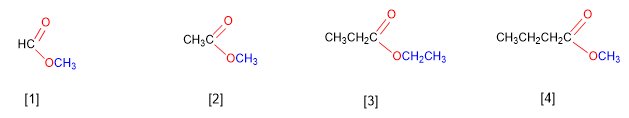
[1] Methyl methanoate
[2] Methyl ethanoate
[3] Ethyl propanoate
[4] Methyl butanoate
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 104033
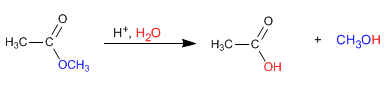
The esters are hydrolyzed in aqueous media, under acid or base catalysis, to yield carboxylic acids and alcohols.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 109124
The esters are hydrolyzed in aqueous media, under acid or base catalysis, to yield carboxylic acids and alcohols. Basic hydrolysis is called saponification and transforms esters into carboxylates.
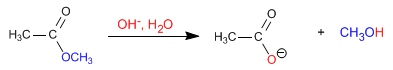
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 57484
Lactones are cyclic esters and hydrolyze in a manner analogous to noncyclic esters, forming compounds containing acid and alcohol groups.
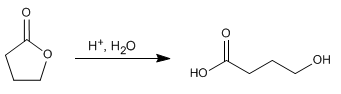
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 51747
Esters react with alcohols in acidic media, replacing their alkoxy group with the corresponding alcohol, as can be seen in the following reaction. This reaction is called transesterification.
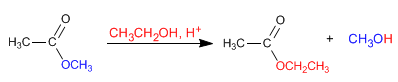
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 37709
Esters transesterify in the presence of alkoxides, depending on the reaction:
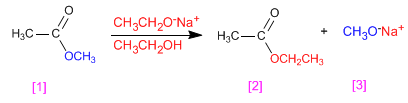
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 38467
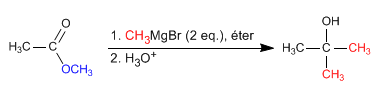
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 52726
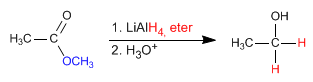
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 49990
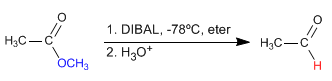
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 28014
The esters have acidic hydrogens with pKa=25 in their position, which can be subtracted using bases. The conjugate base is an enolate ester, a highly nucleophilic species that attacks a varied number of electrophiles.
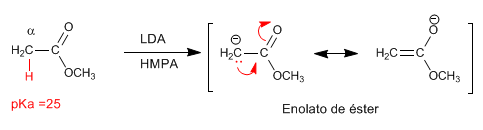
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ESTERS THEORY
- Hits: 60670
When an ester with hydrogens a is treated with an equivalent of base (alkoxide) it condenses to form a product of the family of 3-ketoesters. This type of reaction is known as a Claisen condensation.