ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 22404
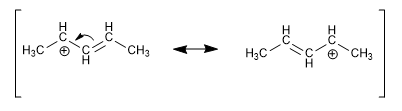
Positive, negative or radical charges in positions close to double bonds are delocalized by resonance, being especially stable.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 41864
The group CH2=CHCH2- is called allyl. Some compounds that derive from the allyl group are:
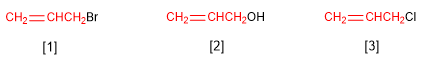
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 25405
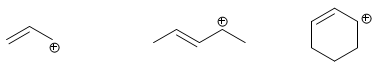
Carbocations formed on carbons located in allylic positions are called allylic cations.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 17994
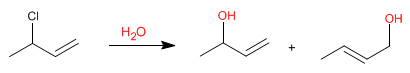
Allylic systems can act as substrates in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Thus, the reaction of 3-chloro-1-butene with water produces two allylic alcohols.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 4382
The formation of the allylic carbocation, stabilized by resonance, allows the reaction to evolve in two ways that lead to the kinetic and thermodynamic products.
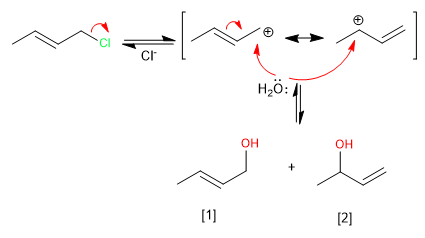
Read more: Kinetic and thermodynamic control in allylic systems
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 3572
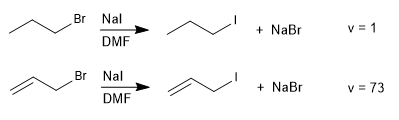
SN2 reactions with leaving groups in allylic positions proceed more rapidly than those for the corresponding saturated haloalkanes.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 5237
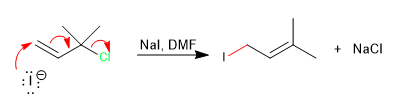
With tertiary allylic substrates and under SN2 conditions (good nucleophile and aprotic solvent), a concerted reaction is produced by the nucleophile attacking the carbon of the double bond with loss of the leaving group.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 3459
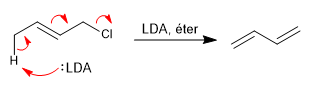
Strong and hindered bases mostly give E2 with allylic systems, deprotonating the carbon located in position 4 with respect to the leaving group.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 4491
Halogens can add to alkenes giving vicinal dihaloalkanes, but when this reaction is carried out at low halogen concentrations, radical mechanisms are favored. A widely used reagent in allylic brominations is NBS (N-bromosuccinimide).
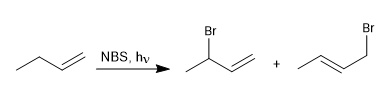
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 3655
The conjugated dienes add the acids of the halogens forming kinetic and thermodynamic products, whose ratio can be controlled with the reaction conditions (temperature and time).
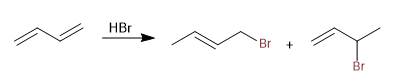
Read more: Acid addition of halogens (HX) to conjugated dienes
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- ALLYLIC SYSTEMS THEORY
- Hits: 4883
Unlike the addition of bromine to alkenes, conjugated dienes do not form halonium ions due to the high stability of the carbocation formed.
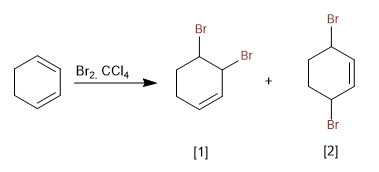
[1] Product of addition 1,2
[2] Addition product 1.4