Chlorine and bromine add to alkenes to give 1,2-dihaloalkanes. For example, 1,2-dichloroethane is synthesized by adding chlorine to ethene. 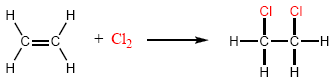
F2 and I2 are not used as reactants in this reaction. Fluor reacts explosively with alkenes and the addition of I 2 is thermodynamically unfavorable.
The mechanism of this reaction involves the formation of the bromonium ion in a first stage. In the second step, Br - acts as a nucleophile, opening the cycle of the bromonium ion to form a 1,2-dibromoalkane.
Stage 1. Double bond attack on the previously polarized bromine molecule.
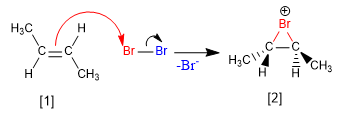
Stage 2. Opening of the halonium (bromonium) ion by bromide attack on the most substituted carbon.
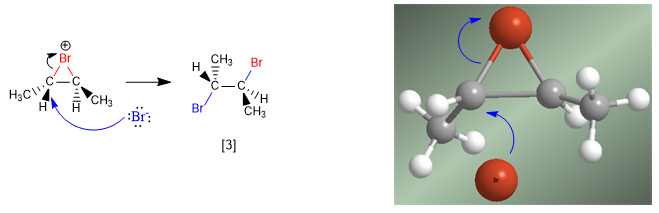
[1] trans-But-2-ene
[2] Bromonium ion.
[3] Dihaloalkane "ANTI"