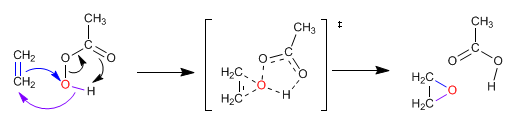
Alkenes react with peracids (peroxyacids) to form epoxides. Epoxides are three-membered cycles that contain oxygen.
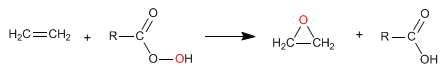
The most common reagent in this reaction is peroxyacetic acid, although MCPBA can also be used. The most commonly used solvents are dichloromethane and chloroform.
The epoxidation of alkenes is chemoselective, reacting better with more substituted alkenes.
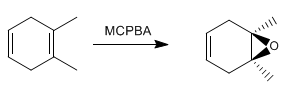
It also presents a high diastereoselectivity, better epoxidizing the less hindered face of the alkene.
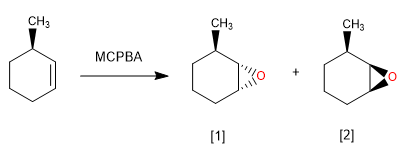
[1] Majority. Epoxidation on the less impeded side.
[2] Minority.
The mechanism of the epoxidation of alkenes is concerted, taking place in a single stage.