Aldol condensation is a reaction of aldehydes or ketones. which forms 3-hydroxycarbonyls (aldols) . 3-hydroxyaldehyde under dehydration conditions by heating yields an alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde . 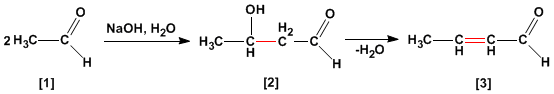
Mechanism
Ethanal is partially transformed into its enolate by the hydroxide anion. The enolate is resonance stabilized. 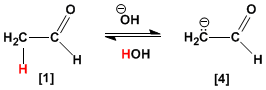
The nucleophilic addition of the enolate ion to the carbonyl group of another ethanal molecule gives the alkoxide . 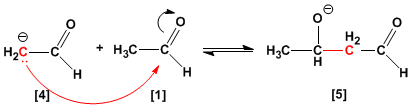
alkoxide formed in the nucleophilic addition step, subtracts a proton from the solvent, generating the product . 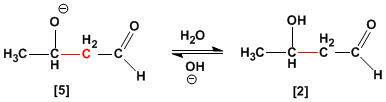
References
1. T. Mukaiyama, Org. react. 1982, 28, 203-331; T. Mukaiyama, S. Kobayashi, Org. react. 1994, 46, 1–103.
2. U. Koert, Nachr. Chem. Techn. Lab. 1995, 43, 1068–1074.