Alkenes can be hydrated with aqueous mercury acetate followed by reduction with sodium borohydride. This reaction produces alcohols and follows the Markovnikov rule.
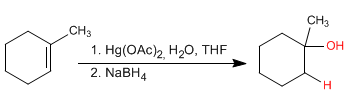
The reaction mechanism begins with the attack of the double bond to the + HgOAc ion from the dissociation of mercury acetate, forming the mercurinium ion that opens by water attack. Sodium borohydride treatment replaces mercury with hydrogen.
Stage 1. Ionization of mercury acetate
Stage 2. Electrophilic addition to the double bond
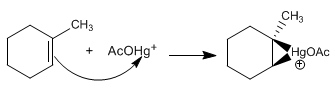
Stage 3. Opening of the mercurinium ion
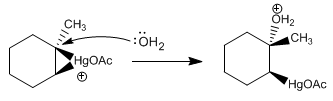
Stage 4. Deprotonation of water
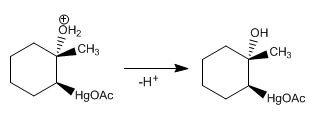
Stage 5. Mercury reduction with sodium borohydride
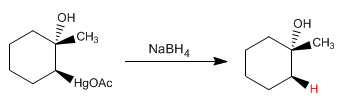
The regiochemistry of the reaction corresponds to a Markovnikov addition of water. Regarding stereochemistry, hydrogen and the hydroxyl group add to Anti.