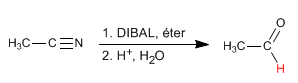NITRILE THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 41775
IUPAC names nitriles by adding the suffix -nitrile to the name of the alkane with the same number of carbons.
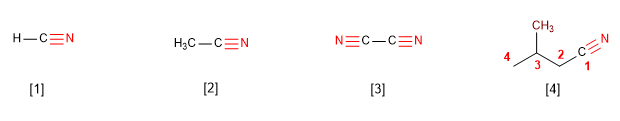
[1] Methanenitrile
[2] Ethanenitrile
[3] Ethanedinitrile
[4] 3-Methylbutanenitrile
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 46920
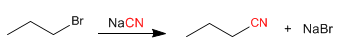
a) From haloalkanes: Nitriles can be prepared from haloalkanes, by SN2 processes. The reaction gives good performance with primary and secondary substrates, the tertiary ones are preferentially eliminated, forming alkenes.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 45107
Nitriles hydrolyze in acidic media, under heating, becoming carboxylic acids and ammonium salts. The hydrolysis of nitriles is an irreversible process.
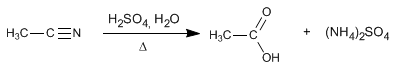
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 36335
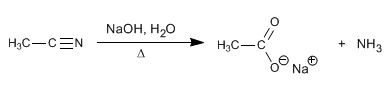
The nitriles are hydrolyzed with aqueous soda, under heating, to form carboxylates and ammonia.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 25794
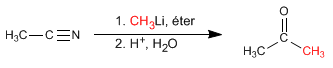
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 17865
Nitriles present hydrogens to acids that can be removed with strong bases, forming nitrile enolates. These hydrogens have a pKa of 25.
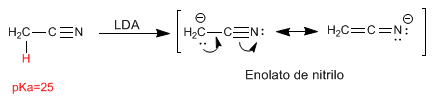
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 28967
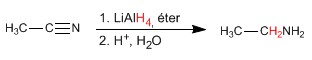
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- NITRILE THEORY
- Hits: 24508
DIBAL (diisobutylaluminum hydride) reduces nitriles to aldehydes