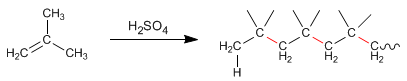THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 119694
The characteristic reaction of alkenes is the addition of substances to the double bond, according to the equation: 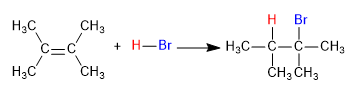
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 130509
Hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen to a double bond to form alkanes.
Platinum and palladium are the most commonly used catalysts in the hydrogenation of alkenes. Palladium is used in the form of powder adsorbed on carbon (Pd/C). Platinum is used as PtO2 (Adams Catalyst). 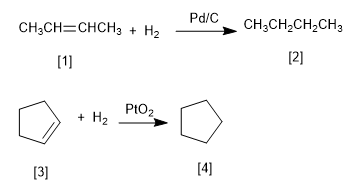
[1] 2-Butene
[2] Butane
[3] Cyclopentene
[4] Cyclopentane
Alkenes are hydrogenated on both sides, producing two enantiomers in equal proportion (racemic mixture).
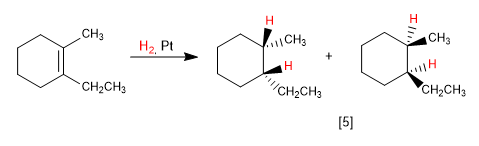
[5] Racemic mixture
When the alkene has one face more hindered than the other, diastereoisomers are obtained in different proportions.
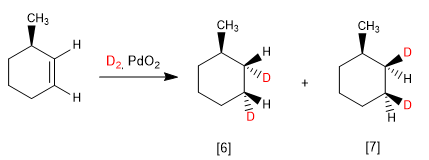
[6] Major product of hydrogenation. The underside of the alkene is less hindered.
[7] Minority product. Hydrogenation occurs on the methyl side, which prevents the approach of the reagent
In bicycles the most favorable face is the one on the side of the bridge:
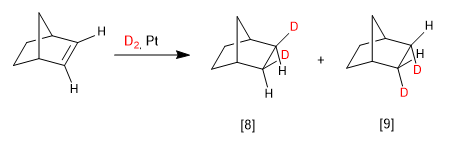
[8] Major product. The bridge of the bicycle is the chain that exerts the least impediment.
[9] Minority product.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 73776
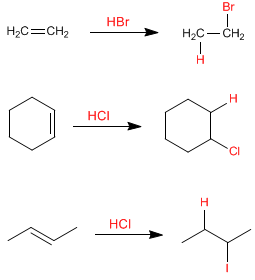
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 97510
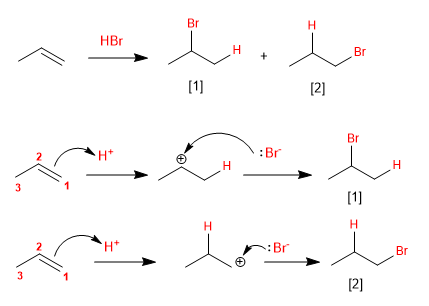
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 136214
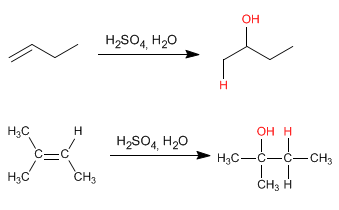
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 101352
Chlorine and bromine add to alkenes to give 1,2-dihaloalkanes. For example, 1,2-dichloroethane is synthesized by adding chlorine to ethene. 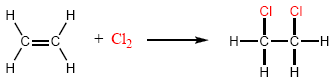
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 72268
Alkenes react with halogens in an aqueous medium to form halohydrins, compounds that contain a halogen and a hydroxyl group in neighboring positions.
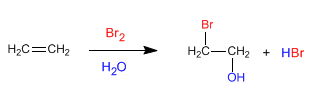
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 59158
Alkenes can be hydrated with aqueous mercury acetate followed by reduction with sodium borohydride. This reaction produces alcohols and follows the Markovnikov rule.
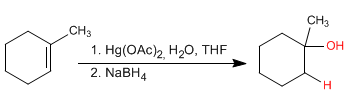
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 72080
Hydroboration is a reaction in which a boron hydride [2] reacts with an alkene [1] to give an organoborane [3] .
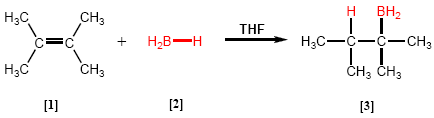
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 61301
The dihydroxylation of an alkene consists of adding an -OH group to each carbon to form vicinal diols. This reaction can be carried out with osmium tetroxide in hydrogen peroxide, or with potassium permanganate in water.
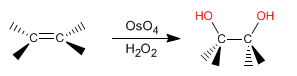
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 77058
Alkenes react with peracids (peroxyacids) to form epoxides. Epoxides are three-membered cycles that contain oxygen.
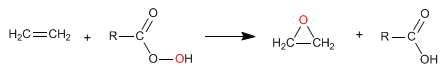
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 128362
Alkenes react with ozone to form aldehydes, ketones, or mixtures of both after a reduction step.
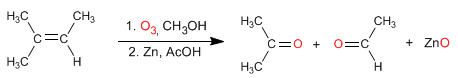
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 77275
In 1929, Professor S. Kharasch of the University of Chicago observed the anti-Markovnikov addition of HBr to an alkene due to the presence of peroxides in the reaction medium.

- Details
- Germán Fernández
- THEORY REACTIONS OF ALKENES
- Hits: 91677
Alkenes, in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, condense to form chains called polymers. Let's see an example with 2-Methylpropene