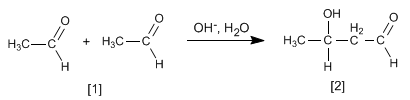
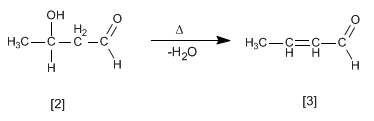
The aldol formed dehydrates in the basic medium by heating to form an a , b -unsaturated.
The aldol condensation mechanism occurs with the formation of an enolate, which attacks the carbonyl of another molecule. In this condensation, a carbon-carbon bond is formed between the carbonyl of one molecule and the a- carbon of the other.
Stage 1. Formation of the enolate
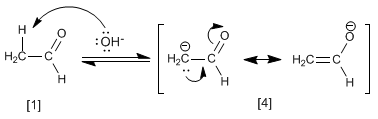
The base depotates the alpha carbon of the ethanal, generating the resonance-stabilized enolate.
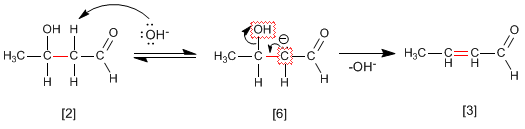
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of the enolate on the carbonyl
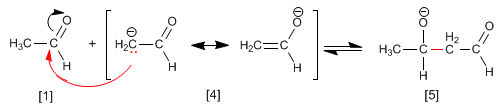
Stage 3. Protonation
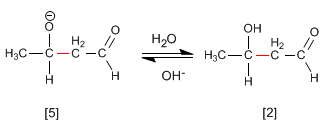
Step 4. Dehydration of the aldol