The reaction of aldehydes or ketones with primary amines generates imines . The reaction is favored in a slightly acid medium (pH=4.5). 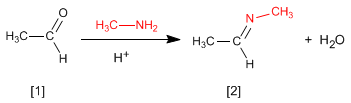
Control of the pH is essential, since protonation of the carbonyl oxygen is required to promote nucleophilic attack.
Mechanism:
Stage 1. Protonation of the carbonyl group that increases the positive polarity on carbon and favors the nucleophilic attack. 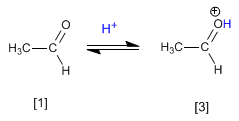
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of the primary amine on the carbonyl carbon. 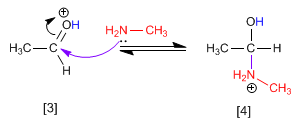
Stage 3. Protonation of the hydroxyl group to transform it into a good leaving group. 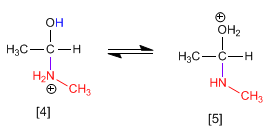
Stage 4. Loss of water and formation of the protonated imine. 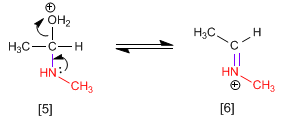
Stage 5. Deprotonation of the cation. 
Video
