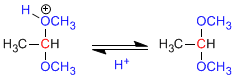Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohols under conditions of acid catalysis, forming hemiacetals in a first stage, which later evolve by reaction with a second equivalent of alcohol to acetals. 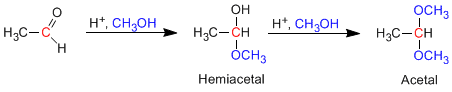
Mechanism for the formation of acetals
Step 1. Protonation of the hydroxyl group 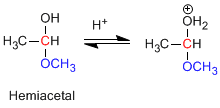
Stage 2. Loss of water. 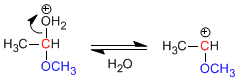
Stage 3. Alcohol attack on the carbocation 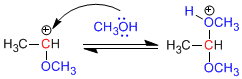
Stage 4. Deprotonation of the acetal