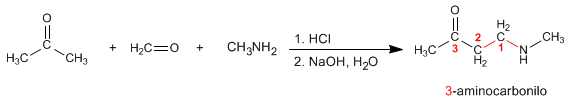AMINES THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 140662
Rule 1. Amines can be named as derivatives of alkylamines or alkanoamines. Let's see some examples.
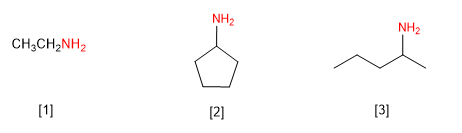
Ethylamine (Ethanamine)
Cyclopentylamine (Cyclopentanamine)
(Pent-2-yl)amine (Pentan-2-amine)
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 122060
Amines have lower melting and boiling points than alcohols. Thus, ethylamine boils at 17ºC, while the boiling point of ethanol is 78ºC.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 75287
Amines have acidic hydrogens on the amino group. These hydrogens can be subtracted using strong bases (organometallic, metal hydrides) forming amides (amine bases).
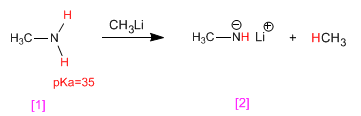
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 74550
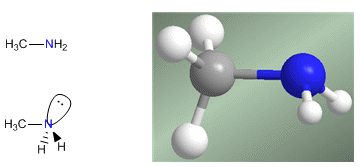
Amines are nitrogenous compounds with a pyramidal structure, similar to ammonia. Nitrogen forms three single bonds through sp 3 -hybridized orbitals. The lone pair occupies the fourth orbital with sp 3 hybridization and is responsible for the basic and nucleophilic behavior of amines.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 58738
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 58155
Nitriles can be prepared by reacting haloalkanes with sodium cyanide. The reduction of nitriles with LiAlH 4 produces amines.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 45760
The reaction of primary and secondary haloalkanes with sodium azide produces alkylazides, which by reduction with LiAlH 4 give rise to amides.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 44169
Amides are reduced with LiAlH 4 to form amines. The carbon number of the final amine is equal to that of the starting amide.
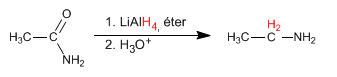
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 44246
Amides are reduced with LiAlH 4 to form amines. The carbon number of the final amine is equal to that of the starting amide.
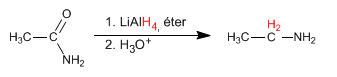
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 42856
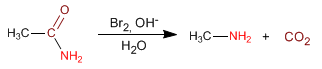
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 60509
The Gabriel synthesis allows primary amines to be obtained from haloalkanes, without the formation of mixtures of secondary and tertiary amines.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 56449
Reductive amination consists of forming an imine, from aldehydes or ketones and amines, which is reduced to an amine in a subsequent stage. This reduction can be carried out with $H_2$ catalyzed by Nickel or with $NaBH_3CN$.
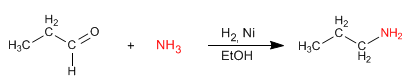
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 35758
Epoxides (oxacyclopropanes) open by nucleophile attack, due to the significant ring strain. If the nucleophile used is ammonia, a β-aminoalcohol is obtained. This type of product can also be obtained by opening the epoxide with sodium azide, and reducing the azide in a second stage.
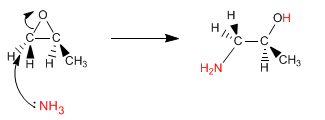
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 64333
The Hofmann elimination allows the conversion of amines to alkenes. It is a regioselective reaction that follows Hofmann's rule, forming the least substituted alkene.
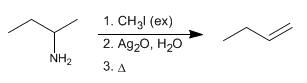
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 44085
The Cope elimination makes it possible to obtain alkenes from tertiary amines. The reaction consists of oxidizing the tertiary amine, forming an amine N-oxide, which is eliminated intramolecularly by heating, giving rise to the alkene.
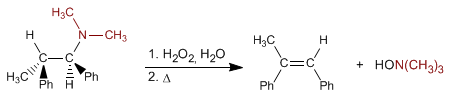
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- AMINES THEORY
- Hits: 48240
Mannich prepares 3-aminocarbonyls from primary or secondary amines, methane, and an enolizable carbonyl. Let's see an example: