Modelle-Alkane
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- Modelle-Alkane
- Zugriffe: 164783
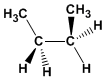
Formel : C 4 H 10
Molekulargewicht : 58.123
Schmelzpunkt: -138,35ºC
Siedepunkt: -0,45 °C
Kommentar: Die gauche-Konformation von Butan wechselt bei 60º mit Methylen. Nach Anti ist es die stabilste Konformation von Butan.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- Modelle-Alkane
- Zugriffe: 160997
Molekulares Butanmodell SIN
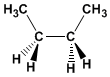
Formel
:
C4H10
Molekulargewicht: 58.123
Schmelzpunkt: -138,35ºC
Siedepunkt: -0,45 °C
Kommentar: Verfinsterte Konformation von Ethan. Die Wechselwirkung zwischen Methylen macht diese Konformation zur instabilsten von Butan.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- Modelle-Alkane
- Zugriffe: 11967

Formel: CH4
Molekulargewicht: 16,0426
Schmelzpunkt: -182,47ºC
Siedepunkt: -161,45 °C
Kommentar: Leicht entzündbares farbloses Gas. Toilette.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- Modelle-Alkane
- Zugriffe: 167332
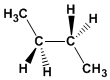
Formel : C4H10
Molekulargewicht: 58.123
Schmelzpunkt: -138,35ºC
Siedepunkt: -0,45 °C
Kommentar: Es ist die stabilste Konformation von Butan. Es zeigt die minimalen Wechselwirkungen zwischen Substituenten.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- Modelle-Alkane
- Zugriffe: 14431
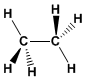
Formel: C 2 H 6
Molekulargewicht: 30,0694
Schmelzpunkt: -183,3ºC
Siedepunkt: -88,6 °C
Kommentar: Farbloses, entzündbares Gas.