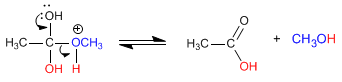The esters are hydrolyzed in aqueous media, under acid or base catalysis, to yield carboxylic acids and alcohols.
In acidic media, the hydrolysis of esters can be written by the following chemical equation:
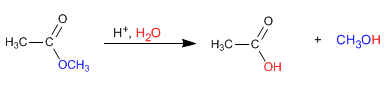
The mechanism of acid hydrolysis occurs in the following stages:
Stage 1. Protonation of the ester
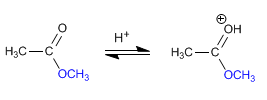
Stage 2. Nucleophilic addition of water to the carbonyl
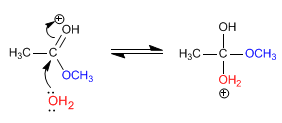
Stage 3. Acid-base balance, which transforms the methoxide into a good leaving group (methanol).
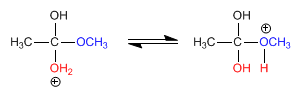
Stage 4. Elimination of methanol