Name the following esters:
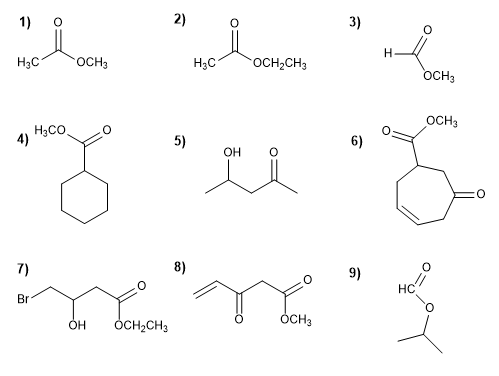
SOLUTION:
Molecule 1.
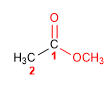
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: no
4. Name: Methyl ethanoate
Molecule 2.
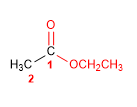
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: no
4. Name: Ethyl Ethanoate
Molecule 3.
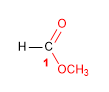
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: no
4. Name: Methyl methanoate
Molecule 4.
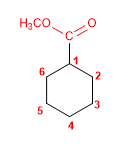
1. Main function: ester (methyl carboxylate)
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locant (without carbon numbering)
3. Substituents: no
4. Name: Methyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate
Molecule 5.
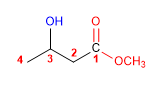
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: 3-hydroxy
4. Name: Methyl 3-Hydroxybutanoate
Molecule 6.
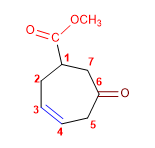
1. Main function: ester (methyl carboxylate)
2. Numbering: Start at the carbon of the ring to which the ester is attached and proceed to give the alkene the lowest locant.
3. Substituents: oxo in 6
4. Name: Methyl 6-Oxocyclohept-3-enecarboxylate
Molecule 7.
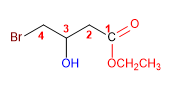
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: 4-bromo and 3-hydroxy
4. Name: Ethyl 4-Bromo-3-hydroxybutanoate
Molecule 8.
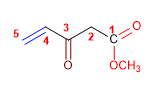
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: ketone (oxo) in 3
4. Name: Methyl 3-Oxopent-4-enoate
Molecule 9.
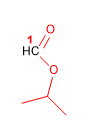
1. Main function: ester
2. Numbering: f. major with minor locator
3. Substituents: no
4. Name: Isopropyl methanoate