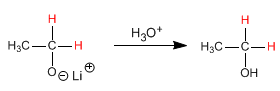Lithium aluminum hydride reduces carboxylic acids to alcohols.
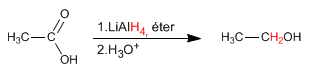
A possible mechanism for this reduction is the following:
Step 1. Deprotonation of the carboxylic acid
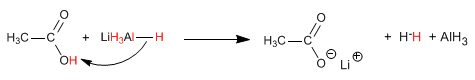
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of the hydride
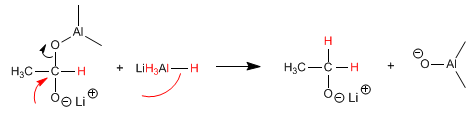
Stage 3. Displacement of oxygen with the hydride ion

Stage 4. Hydrolysis