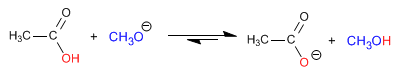The esters are hydrolyzed in aqueous media, under acid or base catalysis, to yield carboxylic acids and alcohols. Basic hydrolysis is called saponification and transforms esters into carboxylates.
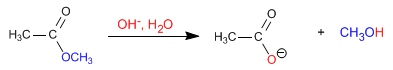
The mechanism of basic hydrolysis occurs in the following stages:
Stage 1. Nucleophilic addition of water to the carbonyl
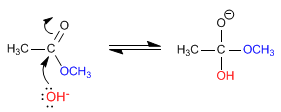
Stage 2. Methoxide removal
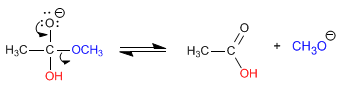
Stage 3. Acid-base balance between carboxylic acid and methoxide. This very favorable balance displaces the previous balances towards the final product.