Alkanoyl halides are obtained by reacting carboxylic acids with PBr 3 . SOCl 2 can also be used.
Thus, ethanoic acid is transformed into ethanoyl bromide by reaction with phosphorous tribromide. Ethanoic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to form the compound
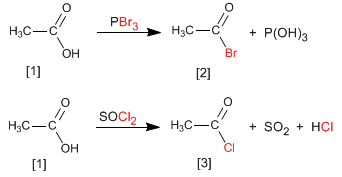
The reaction mechanism consists of the nucleophilic attack of the carboxylic acid on the phosphorus or sulfur of the reagent, producing an addition-elimination mechanism that leads to the alkanoyl halide.
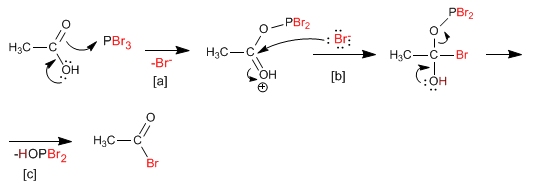
[a] Acid attack on phosphorus tribromide.
[b] Nucleophilic addition step.
[c] Elimination step
This mechanism is repeated three times, replacing all the bromines of the phosphorus tribromide with hydroxy groups.
Thionyl chloride has a mechanism analogous to that of phosphorus tribromide, converting carboxylic acids to alkanoyl chlorides. The byproducts formed in this reaction are sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride.
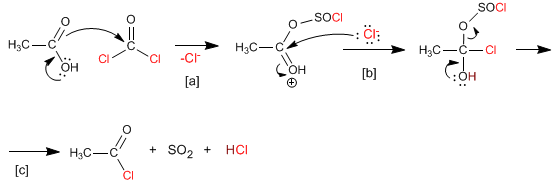
[a] Acid attack on thionyl chloride.
[b] Nucleophilic addition
[c] Elimination
