Esters are obtained by reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols in the presence of mineral acids. The reaction is carried out in excess of alcohol to shift the equilibria to the right. The presence of water is detrimental since it hydrolyzes the ester formed.
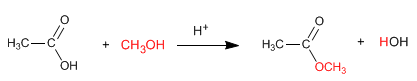
The reaction that prepares esters from carboxylic acids is called esterification and has the following mechanism:
Step 1. Protonation of the carboxyl group
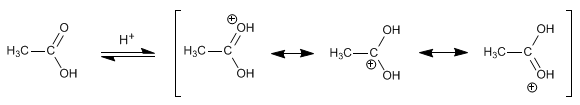
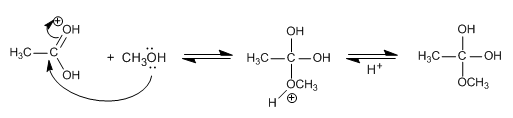
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of methanol to the carbon of the carboxyl group (Addition)
Stage 3. Water removal
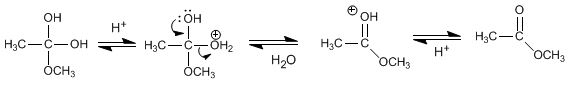
Another synthesis method consists of a nucleophilic substitution, using the carboxylate ion as the nucleophile.
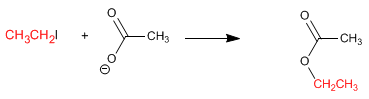
This reaction works well with both primary and secondary substrates.