Esters come from condensing acids with alcohols and are named as salts of the acid from which they come. IUPAC nomenclature changes the -oic ending of the acid to -oate , ending with the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen.
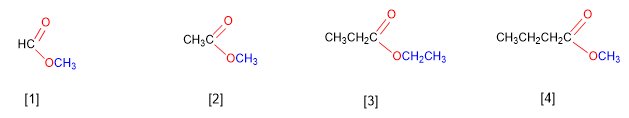
[1] Methyl methanoate
[2] Methyl ethanoate
[3] Ethyl propanoate
[4] Methyl butanoate
Esters are priority groups over amines, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, nitriles, amides, and alkanoyl halides. These groups are named as substituents with the ester being the functional group.
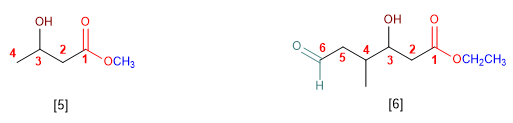
[5] Methyl 3-hydroxybutanoate
[6] Ethyl 3-hydroxy-4-methyl-6-oxohexanoate
Carboxylic acids and anhydrides have priority over esters, which are named as substituents ( alkoxycarbonyl..... )

[7] 5-Methoxycarbonylpentanoic acid
[8] 5-Methoxycarbonylpentanoic acid
When the ester group is attached to a ring, the ring is named as the main chain and the ending -alkylcarboxylate is used to name the ester.

[9] Methyl Benzenecarboxylate (Methyl Benzoate)
[10] Ethyl 4-Bromo-3-methylcyclohexanecarboxylate