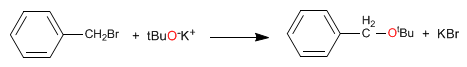The reaction between a primary haloalkane and an alkoxide (or alcohol in a basic medium) is the most important method for preparing ethers. This reaction is known as the Williamson synthesis.
This reaction proceeds through the SN2 mechanism.
The strong basicity of alkoxides leads to elimination reactions with secondary and tertiary substrates, forming alkenes instead of ethers.
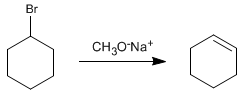
Another situation in which Williamson does not yield ethers is in the case of using hindered alkoxides, such as potassium tert-butoxide. Due to its large size tert -butoxide eliminates even with primary substrates.
With primary haloalkanes and especially with haloalkanes that lack b-hydrogens, Williamson's performance is very good.