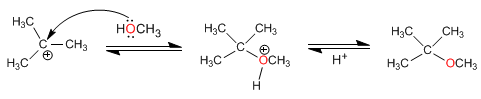
1. Ethers from primary alcohols
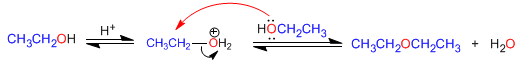
Symmetrical ethers can be prepared by condensation of alcohols. The reaction is carried out under heating (140°C) and with acid catalysis. Thus, two molecules of ethanol condense to form diethyl ether.
The reaction mechanism occurs in the following stages:
2. One of the alcohols is secondary or tertiary
In this case, the reaction takes place under milder conditions, through SN1 mechanisms.
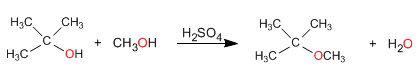
The mechanism occurs with the formation of a highly stable tertiary carbocation
Stage 1. Protonation of the tertiary alcohol
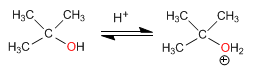
Stage 2. Formation of the carbocation by loss of water
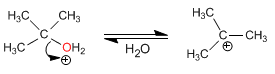
Stage 3. Nucleophilic attack of methanol