The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction makes it possible to halogenate the a-position of carboxylic acids. Phosphorus-catalyzed bromine is used as the reagent. Phosphorus in the presence of bromine generates phosphorus tribromide, which is actually the compound that acts as a catalyst.
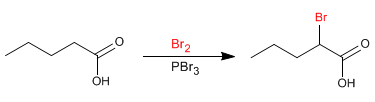
The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky mechanism occurs in four stages.
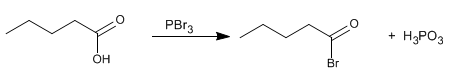
Stage 1. Formation of the alkanoyl bromide
Stage 2. Enolization of the alkanoyl halide
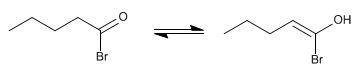
Stage 3. Halogenation of the position a
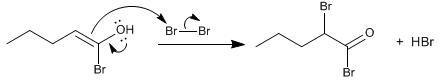
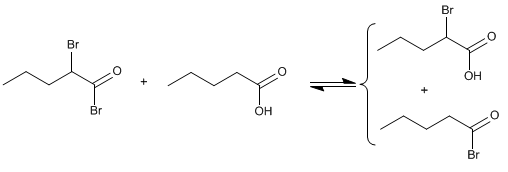
Stage 4. Exchange