Alkynes can be prepared by double dehydrohalogenation of vicinal or geminal dihaloalkanes.
Double elimination from geminal dihaloalkanes
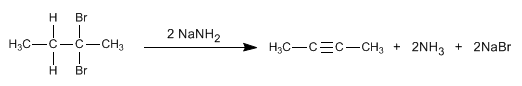
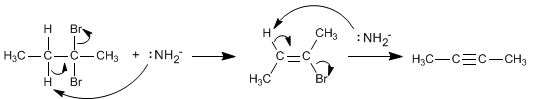
The mechanism of this reaction consists of two successive E2 deletions. In the first elimination the disposition of the leaving group with respect to the subtracted hydrogen must be anti.
Double elimination from vicinal dihaloalkanes
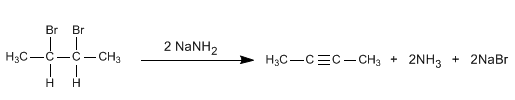
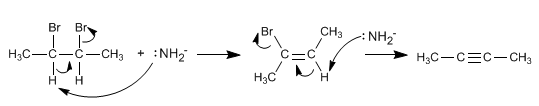
By means of double elimination, the triple bond between the carbons that have the bromines attached will be obtained.
To obtain terminal alkynes from vicinal or geminal dihaloalkanes it is necessary to use 3 equivalents of sodium amide, due to the presence of acidic hydrogen in the alkyne.
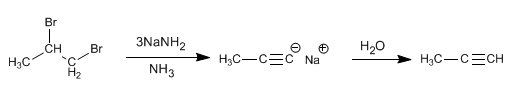
Double elimination to form terminal alkynes can also be done with potassium tert-butoxide in DMSO.