Indicate the most probable major products that are formed when treating the following haloalkanes with sodium ethoxide in ethanol or with potassium tert-butoxide in 2-methyl-2-propanol. a) chloromethane, b) 1-bromopentane, c) 2-bromopentane, d) 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane, e) (1-bromoethyl)cyclopentane, f) (2R,3R)-2-chloro-3-ethylhexane .
SOLUTION:
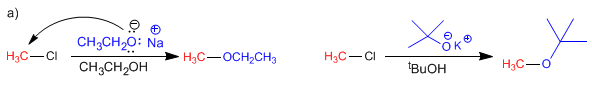
Chloromethane cannot remove by lacking the b -carbon. Even hindered bases such as potassium tert-butoxide give substitution with this type of substrate.
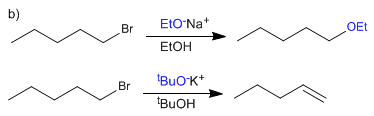
Sodium ethoxide gives S N 2 with primary substrates, while potassium tert-butoxide gives mostly elimination (E2).
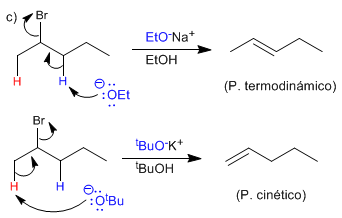
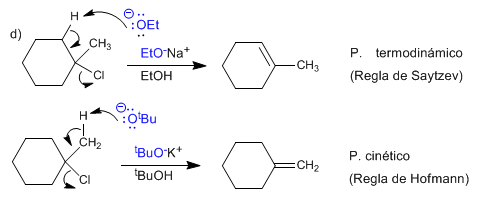
The ethoxide subtracts the innermost hydrogen from the molecule, forming the more stable alkene (thermodynamic product). This reaction is said to follow Saytzev's rule.
Potassium tert -butoxide is a hindered base that removes the most accessible hydrogen faster, forming mainly the less stable alkene (kinetic product). This reaction is said to follow Hofmann's rule.