Primary Substrates: Primary substrates have a single carbon chain on the alpha carbon. The outgoing group is not taken into account.
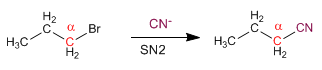
Primary substrates give SN2 with good nucleophiles, such as: I- , Cl- , Br- , NH3 , N3- , CN- , HS- , CH3S- , OH- , CH3O- , NH2- .
Primary substrates do not react with bad nucleophiles: water, alcohols, and acetic acid.
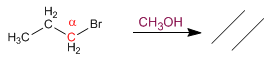
Primary substrates give E2 with hindered bases: potassium tert-butoxide and LDA
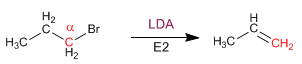
Secondary Substrates: Secondary substrates have two chains on the alpha carbon.
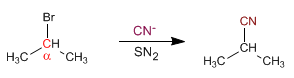
Secondary substrates give S N 2 with good nucleophiles other than strong bases, such as: I- , Cl- , Br- , NH3 , N3- , CN- , HS- , CH3S-
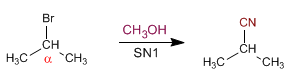
Secondary substrates give SN1 with bad nucleophiles: water, alcohols, and acetic acid
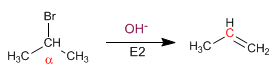
Secondary substrates give E2 with strong and hindered bases: OH- , CH3O- , NH2- , tBuO- , LDA
Tertiary Substrates: Tertiary substrates have three chains on the alpha carbon.
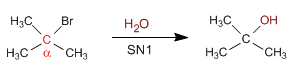
Tertiary substrates give SN1 with weak bases: I- , Cl- , Br- , water and alcohols
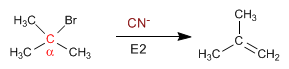
Tertiary substrates are mostly eliminated with the rest of the species: CN- , NH3 , HS- , N3- , CH3S- , OH- , CH3O- , NH2- , tBuO- , LDA
Strong bases, OH- , CH3O - and NH2- , and hindered bases, tBuO- and LDA, give 100% E2. The rest of the bases give mixtures E1, E2, increasing the percentage of E2 with the strength of the base.