An alternative to hydrogenation with Lindlar's catalyst is the reduction of alkynes with sodium or lithium in liquid ammonia, the difference lies in the alkene obtained. Thus, hydrogenation with Lindlar's catalyst produces cis alkenes, while hydrogenation with sodium in liquid ammonia generates trans alkenes.
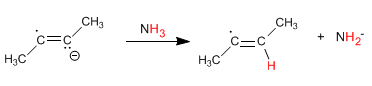
The one-electron reduction occurs through an intermediate called an anion-radical. Protonation of the anion with ammonia produces hydrogenation of the alkene.
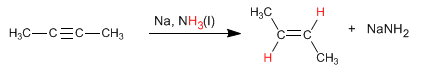
The mechanism of the reaction occurs with the following stages:
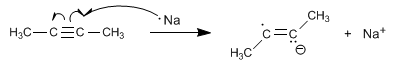
Stage 1 . Formation of the anion-radical by transfer of an electron from sodium to the alkyne.
Stage 2. Protonation of the radical anion with ammonia
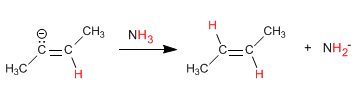
Stage 3 . Transfer of an electron from sodium to the radical forming an anion.
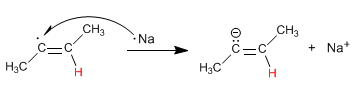
Stage 4. Protonation of the anion with ammonia