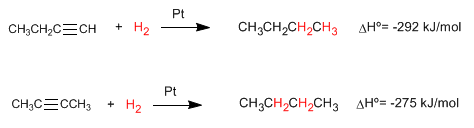
Hydrogenation is an exothermic reaction, and the heat given off is affected by the alkyne substituents. Thus, the internal alkynes give off less heat when hydrogenated than the terminal ones, due to their greater stability due to the phenomenon of hyperconjugation.