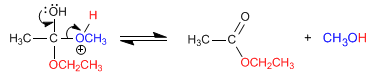Esters react with alcohols in acidic media, replacing their alkoxy group with the corresponding alcohol, as can be seen in the following reaction. This reaction is called transesterification.
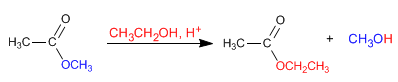
The mechanism of acid transesterification occurs in the following stages:
Stage 1. Protonation of the ester
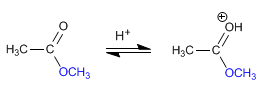
Step 2. Nucleophilic addition of the alcohol to the carbonyl
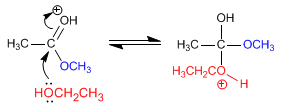
Stage 3. Acid-base balance, which transforms the methoxide into a good leaving group (methanol).
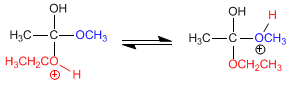
Stage 4. Elimination of methanol