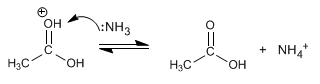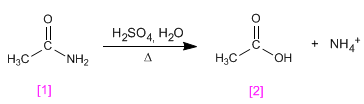
Ethanamide hydrolyzes in a sulfuric medium to form ethanoic acid .
The reaction mechanism occurs in the following steps:
Stage 1. Protonation of carbonyl oxygen.
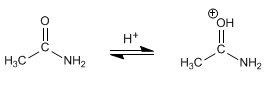
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of water on the carbonyl carbon
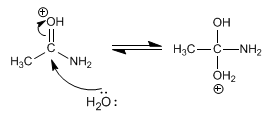
Stage 3. Deprotonation of water and protonation of the amino group.
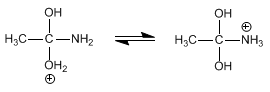
Stage 4. Elimination of ammonia
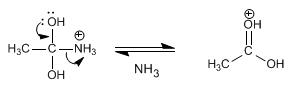
Step 5. Deprotonation of carbonyl oxygen