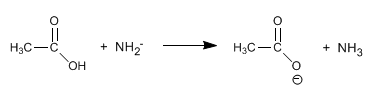The amides are transformed into amines and carboxylic acids by treatment with aqueous soda under heating.
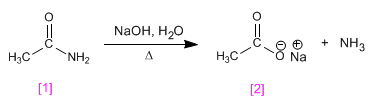
Ethanamide hydrolyzes in the presence of aqueous soda to form sodium ethanoate.
The reaction mechanism occurs in the following steps:
Stage 1 . nucleophile attack
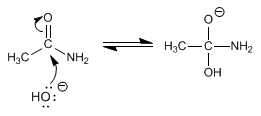
Stage 2 . Elimination
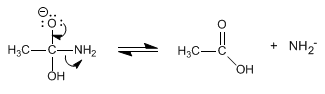
Stage 3. Shifted acid-base balance.