Synthesis of heterocycles with several heteroatoms
Heterocyclic compounds, as already mentioned, have a wide range of applications: they predominate among the compounds used as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and for veterinary use; they are used as polishing additives, antioxidants, corrosion inhibitors, as dyes and pigments; and in many more applications.
Therefore, it is reasonable that currently much of the research in chemistry deals with the synthesis and properties of heterocyclic compounds. To this end, this article is oriented, which aims to provide chemistry students with basic retrosynthesis tools.
The disconnection process for molecules with several heteroatoms can be carried out for each carbon-heteroatom bond, according to the previously studied models or simultaneously, for which affordable polyheteroatom reagents are used.
1. Distance heteroatoms (1, 2)
The most representative and usual reagents are hydrazines and substituted hydrazines, as well as hydroxylamines.
hydrazine |
hydroxylamine |
Propose a synthesis design, from simple materials, for the following molecules:
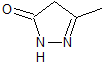
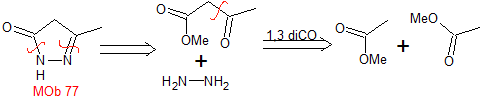
mob 77
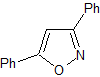
pyrazoles | MOb 78
isoxazoles | MOb 79
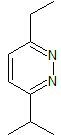
pyridazines |
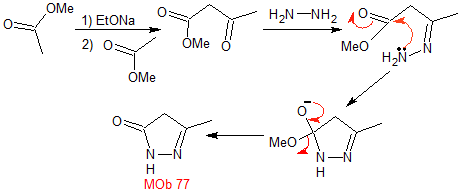
MOb 77 . Retrosynthetic analysis. MOb is a pyrazole derivative and is directly disconnected by CN bonds, to generate simple precursors such as hydrazine and a 1,3-diCO compound.
|
synthesis . Methyl acetate is a good precursor to form the compound 1,3-diCO, which combines with hydrazine to generate MOb 77. |
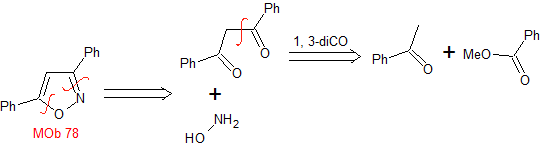
MOb 78- Retrosynthetic analysis .
|
Synthesis. Bezophenone and ethyl benzoate make it possible to form the required 1,3-diCO, to react in a slightly acidic medium with hydroxylamine and after adding NaH, cyclization occurs, which requires more acid to
dehydrate and finally produce
|
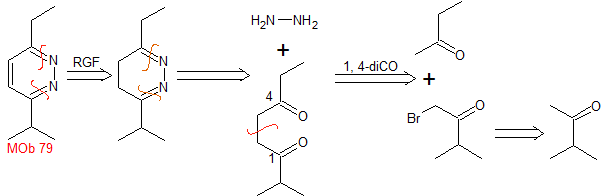
MOb 79 . Retrosynthetic analysis. MOb is a derivative of diazine, which by simultaneous CN disconnection, makes it possible to ensure that the cycloaddition has occurred between hydrazine and a 1,4-diCO compound.
|
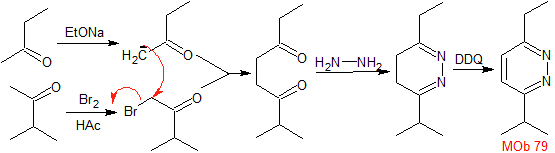
Synthesis : Butanone allows the creation of the 1,4-diCO compound, which is then combined with hydrazine, to form a hydrodiazine, which, oxidized with DDQ, generates
|
1. Distance Heteroatoms (1,3)
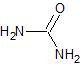
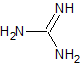
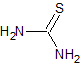
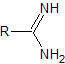
The most significant reagents that contain heteroatoms at a distance of 1.3 or are intercalated with respect to each other are: urea and its derivatives, guanidine and derivatives, thiourea and derivatives, amidines and derivatives, and finally, sodium cyanamide.
urea |
guanidine |
thiourea |
amidines |
sodium cyanamide |
Propose a synthesis for the following molecules:
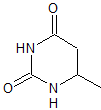
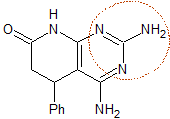
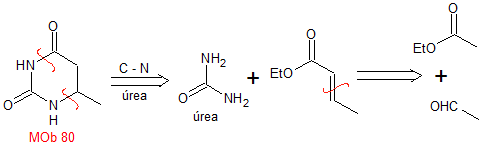
MOb 80
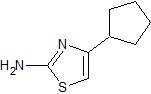
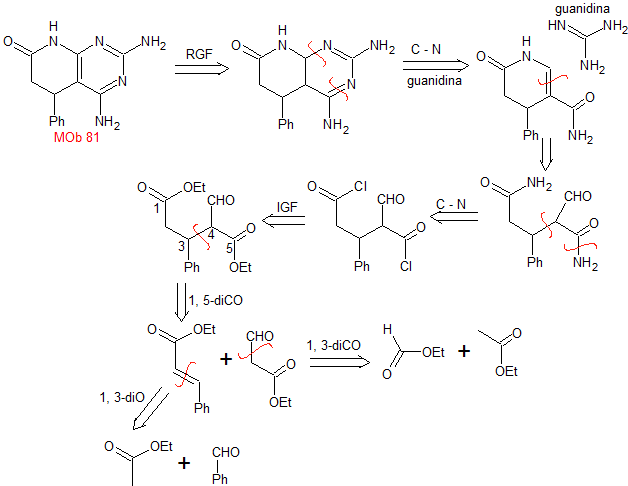
| MOb: 81
| MOb: 82
|
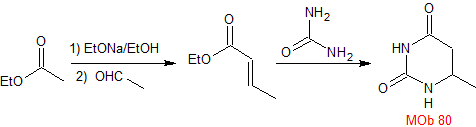
MOb 80 . Retrosynthetic analysis. In the MOb, the structure of urea can be visualized, which invites us to propose two simultaneous CN disconnections.
|
Synthesis. It starts with a Claisen-Schmidt condensation, between an ester and an aldehyde, to then combine the product with urea, by the Michael reaction, to arrive at
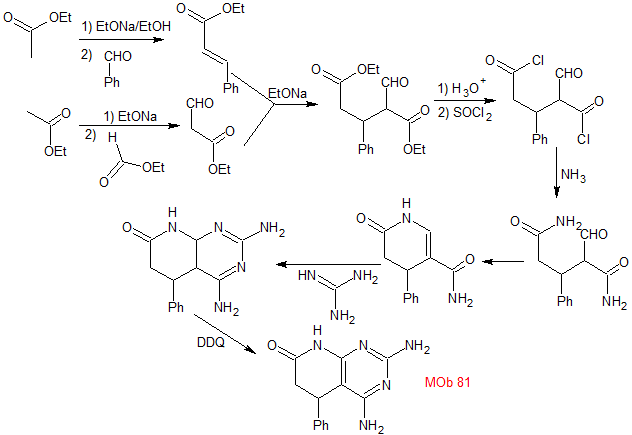
MOb 81 . Retrosynthetic analysis . Initially, an RGF is carried out in the MOb, to generate a precursor carrying the guanidine group, which is why a simultaneous CN disconnection is carried out, to continue the disconnection by the enamine formed. The 1,5-diCO ratio is the best to continue disconnecting and producing structures with dioxygen ratios of 1.3. This leads to simple molecules, as starting materials.
|
Synthesis. The Claisen and Claisen-Schmidt condensations allow obtaining a key intermediate, which is easily transformed into a diester, which after hydrolysis combines with SOCl2 to form a dihalogenated molecule that is transformed into a diamide with ammonia.
The intramolecular reaction of the previous product produces the suitable substrate that reacts with guanidine. The product thus formed is then subjected to an "aromatization process" with DDQ, to form
|
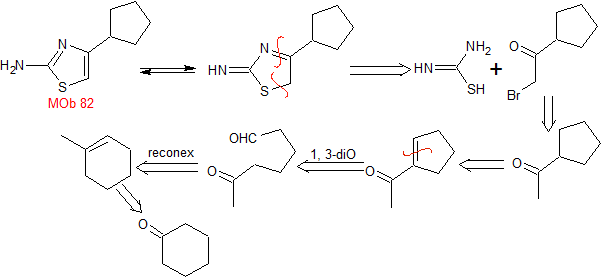
MOb 82. Retrosynthetic analysis. A tautomer of
|
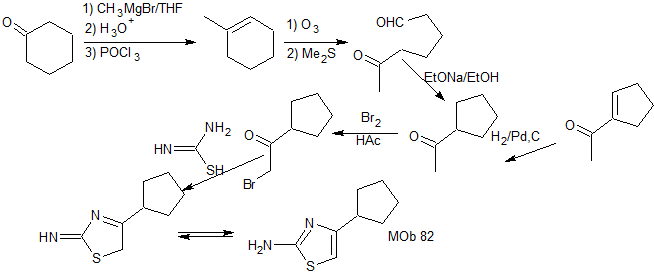
synthesis . Cyclohexanone is the simple starting material that, after several reactions, is opened by ozonolysis in a dimethyl sulfide medium, to produce a 1,6-diCO compound, which is condensed in a basic medium to give the indicated ketone, for its bromination and subsequent reaction with thiourea to form
|
2. Distance heteroatoms (1, 4)
ethylenediamine |
o- phenylenediamine |
X = 0, S |
Propose a synthesis design, for the following molecules:
MOb: 83
| MOb: 84
| MOb: 85
|
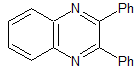
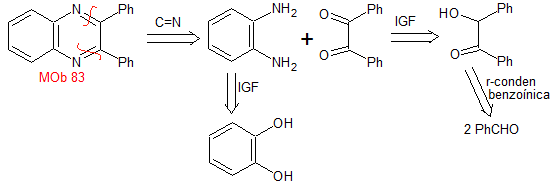
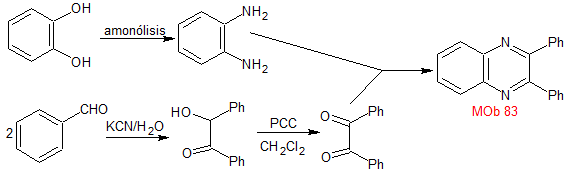
MOb 83 . Retrosynthetic analysis. The imine bonds of the MOb are directly disconnected, which produces two structures of precursor molecules, whose synthesis is simple.
|
synthesis . The benzoinic condensation of benzaldehyde allows reaching the necessary dicarbonyl compound, to be combined with o-phenylenediamine, prepared by ammonolysis of pyrocatechol, to form
|
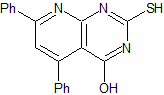
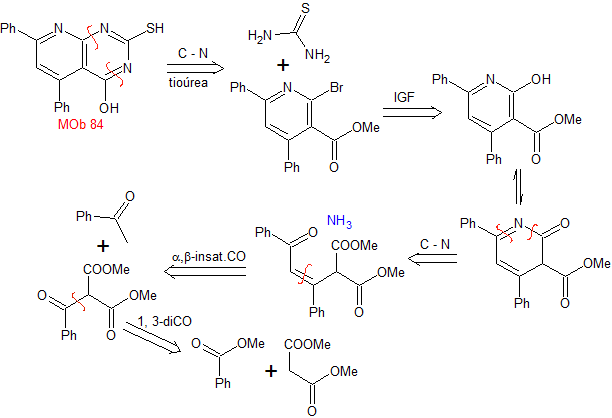
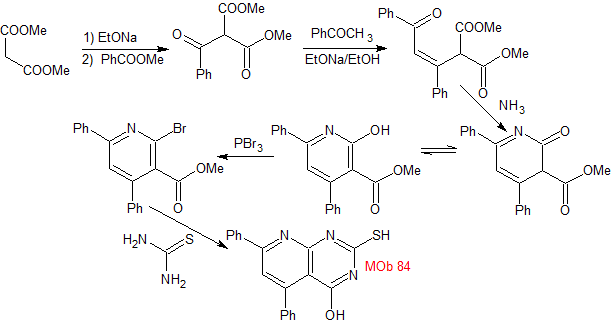
MOb 84 - Retrosynthetic analysis. Again in the MOb the structure of a thiourea can be distinguished, for which reason it is disconnected by the CN bonds. The functionalization of the brominated synthetic equivalent allows us to arrive at structures with dioxygenated ratios, easy to handle in their disconnections.
synthesis . Thus, dimethyl malonate turns out to be the simple starting material for the preparation of MOb 84.
|
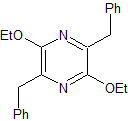
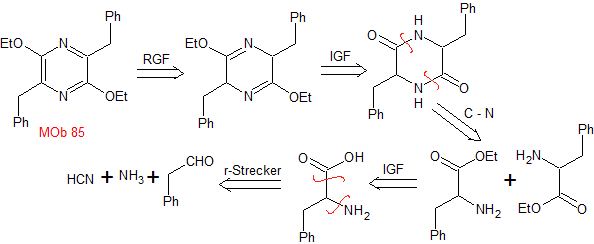
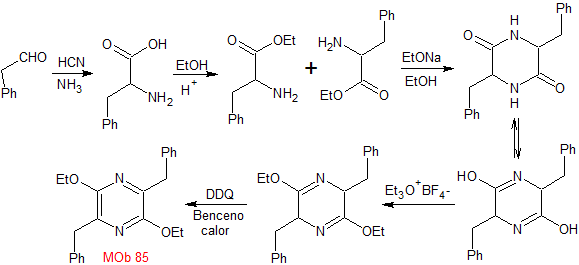
MOb 85 . Retrosynthetic analysis. The MOb is a pyrazine derivative, it is functionalized to reach a precursor that contains two imine groups. The disconnection of the molecule by these bonds allows the generation of another precursor that is an alpha amino ester, the molecule that self-condenses.
|
synthesis . The Strecker synthesis is used to form the required amino ester, which self-condenses in a basic medium. The Et 3 ONF 4 , allows reaching the diiminic compound that is then oxidized or aromatized by the DDQ, to form MOb 85.
|