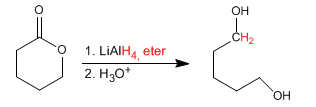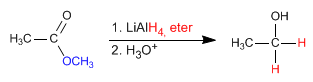
The reductant supplies hydride ions to the carbonyl carbon, transforming it into alcohol.
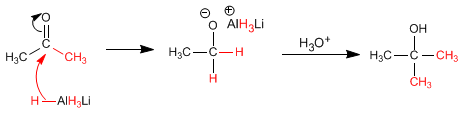
The reaction mechanism is described below:
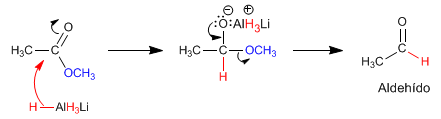
The ketone is more reactive than the ester and a second equivalent of magnesium attacks it to form the alcohol.
Cyclic esters (lactones) reduce with lithium aluminum hydride to form diols.