Write the reaction products of 2-methyl-1-pentene with each of the following reagents: (a) H2 , PtO2 (b) D2 , Pd-C; (c) 1. BH3 , 2. H2O2 /NaOH; (d) HCl; (e) HBr; (f) HBr, ROOR; (g) HI, ROOR; (h) H2SO4 , H2O; (i) Cl2 ; (j) ICl; (k) Br2 , EtOH; (l) 1. Hg(OAc)2 , H2O, 2. NaBH4 ; (m) MCPBA; (n) OsO4 (cat.), H2O2 ; (o) 1. O3 , 2. Zn, AcOH; (p) CH3SH, ROOR; (q) HCBr3 , ROOR; (r) H2SO4 (cat.)
SOLUTION:
a) H2 , PtO2 :
a) H2 , PtO2 :
The hydrogenation of alkenes is a syn reaction. The absence of chiral centers in the product prevents the formation of enantiomers.
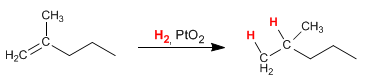
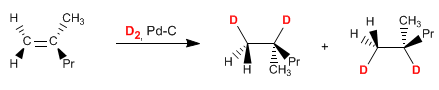
(b) D2 , Pd-C
Deuterium is added in a similar way to hydrogen (syn), but in this case the product has a chiral center (right carbon) that causes the formation of two enantiomers, when deuterium is added on both sides of the alkene.
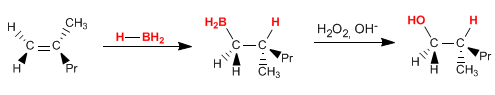
(c) 1. BH3 , 2. H2O2 /NaOH
Hydroboration is a syn and anti Markovnikov reaction. The presence of a chiral center in the product (right carbon) causes the formation of two enantiomers in equal proportion. In the indicated solution, only the product resulting from the addition from the top is drawn.
(d) HCl
The addition of HCl to alkenes is a Markovnikov reaction. Hydrogen adds to the less substituted carbon, forming a carbocation that is attacked in a later stage by halogen. In this case, the attack on both sides produces the same product.
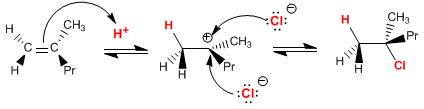
(e) HBr
The addition of HBr to an alkene follows a mechanism analogous to the addition of HCl.
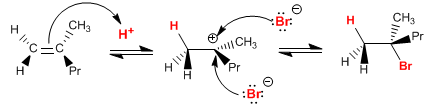
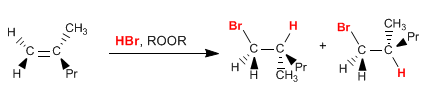
(f) HBr, ROOR
HBr in the presence of peroxides adds anti-Markovnikov. It is a reaction with a radical mechanism.