Enolates of aldehydes or ketones add to the a,b-unsaturated to form 1,5-dicarbonyls. This reaction is called the Michael addition. 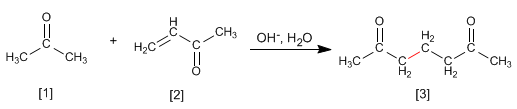
Propanone reacts with a,b-unsaturated to form 1,5-dicarbonyl
Michael Addition Mechanism:
Stage 1. Formation of the enolate. 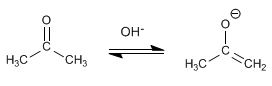
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of the enolate to carbon b of the a,b-unsaturated. 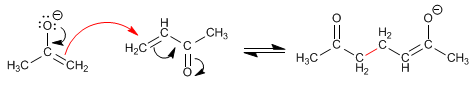
Stage 3. Acid-base balance 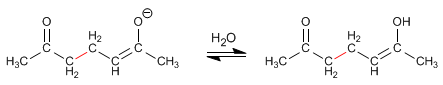
Stage 4. Keto-enol tautomerism 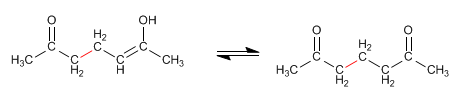
![]() The Michael product can condense via an intramolecular aldol, forming an a,b-unsaturated. The set of the Michael addition and the final aldol is known as the Robinson reaction
The Michael product can condense via an intramolecular aldol, forming an a,b-unsaturated. The set of the Michael addition and the final aldol is known as the Robinson reaction