a) Basicity
Quinoline and isoquinoline behave like bases through the lone pair of nitrogen. In acid media they are protonated to form quinolinium and isoquinolinium salts.
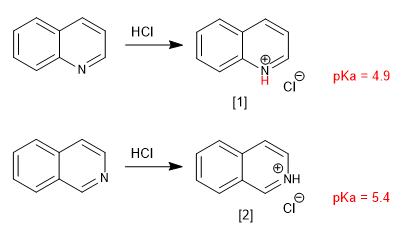
quinolinium salt
isoquinolinium salt
Substituents modify basicity in a manner analogous to pyridine. Donor groups increase the basicity and attractor groups decrease it.
b) Alkylation and acylation
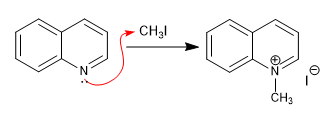
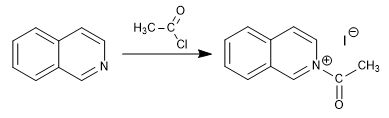
Quinoline and isoquinoline act as nucleophiles through the nitrogen atom, giving rise to alkylation and acylation reactions that form quinolinium and isoquinolinium salts.
a) Alkylation of the quinoline
b) Acylation of isoquinoline
c) Reaction with Lewis acids
Both quinoline and isoquinoline react with Lewis acids via the lone pair on nitrogen.
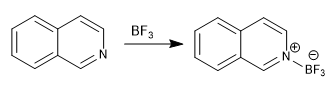
d) Formation of N-oxides
Quinoline and isoquinoline react with hydrogen peroxide or peracids to form quinoline or isoquinoline N-oxides.
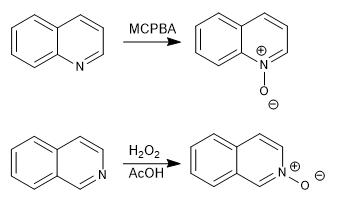
The N-oxides can be reduced back to the original molecules with PPh 3 .