The synthesis of compounds is one of the most important parts of organic chemistry. The first organic synthesis dates back to 1828, when Friedrich Wöhler obtained urea from ammonium cyanate. Since then more than 10 million organic compounds have been synthesized from simpler compounds, both organic and inorganic.
Access the Organic Synthesis section created and maintained by Professor Wilbert Rivera Muñoz
Among the compounds obtained by organic chemists in recent years, one can cite molecules of great practical importance, such as saccharin. Others are mainly of theoretical interest, such as the Cuban one, which allows the study of reactivity and bonding in highly stressed molecules.
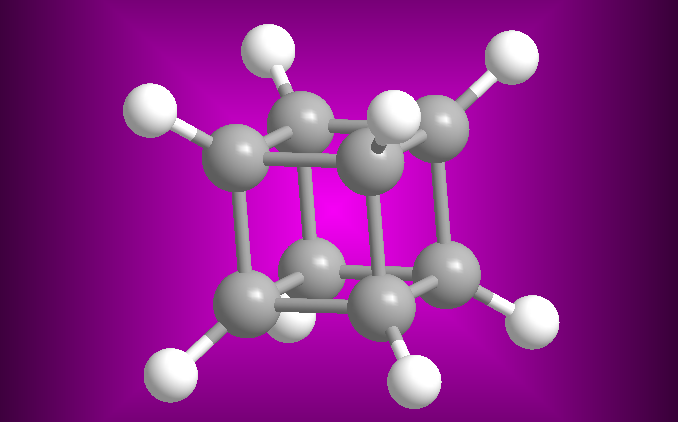
 Cuban molecular model
Cuban molecular model
The Cuban (C 8 H 8 ), receives this name from its cube shape. Each vertex is formed by a carbon that is linked to three other identical ones and to a hydrogen. For a long time it was considered a theoretical molecule, until it was synthesized in 1964 by Professor Philip E. Eaton of the University of Chicago.
Next, the synthesis of the Cuban is detailed. Surprising compound, whose existence makes clear the enormous synthetic possibilities that organic chemistry offers us.
The synthesis carried out by Dr. Philip E. Eaton, starts from 2-cyclopentenone. In the first stage, the allylic position is halogenated with NBS. The second step consists of the halogenation of the alkene and in a last stage a double elimination promoted by triethylamine is carried out. 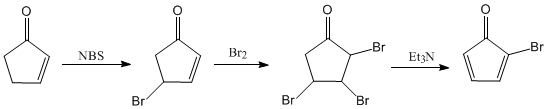
In the previous steps we obtained a diene, which condenses with itself through the Diels - Alder reaction 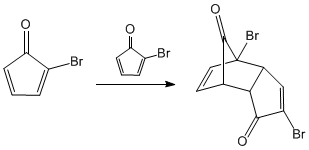
Protection of the carbonyl group located on the bridge of the bicycle, using ethanediol as a reagent in an acid medium. The protective group formed is an acetal, very stable in basic media. 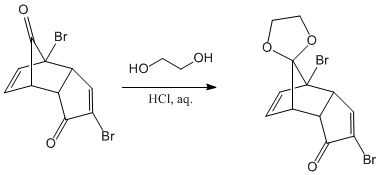
Photochemical reaction [2+2]. In it two alkenes are united forming cycles of four 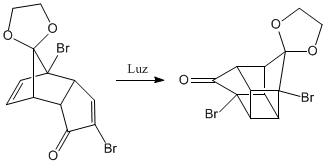
Oxidation of the ketone to carboxylic acid. 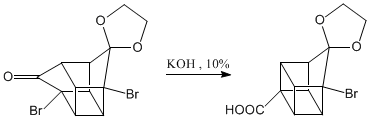
The three steps that follow remove the acid group from the molecule. Reaction called decarboxylation. 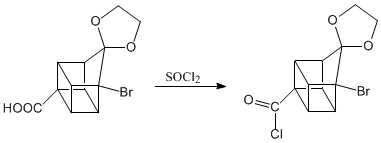

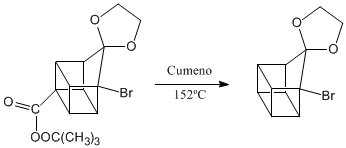
Deprotection of the carbonyl group. 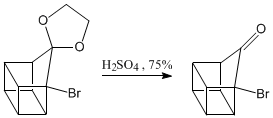
Oxidation of the ketone to carboxylic acid. 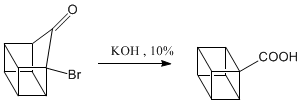
Decarboxylation stages. 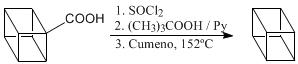
I see that you have had the patience to reach the end of this synthesis. I imagine that it seems very complicated to you, am I wrong?
The Cuban synthesis is based on quite elementary reactions, all of them studied in the first courses of organic chemistry, which every chemist should know. The great difficulty of this synthesis (or of any other), is in choosing the appropriate starting reagent and the sequence of reactions that will lead us to the final product. That is where the difficulty of any synthesis lies.
The most important purpose of this website is to present the main reactions of organic compounds, making them familiar to the student through a multitude of examples.
My wish is that after reviewing these pages, you can successfully face the synthesis of relatively complex molecules, just like Philip E. Eaton did in 1964 with the Cuban. You have 10 million organic compounds that have already been synthesized to practice.