 The pyridine molecule can be obtained by reacting enamines with a,b-unsaturated. Thus, the reaction between ethenamine and propenal, followed by oxidation, produces pyridine.
The pyridine molecule can be obtained by reacting enamines with a,b-unsaturated. Thus, the reaction between ethenamine and propenal, followed by oxidation, produces pyridine.
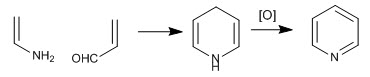
The following lines detail the synthesis mechanism:
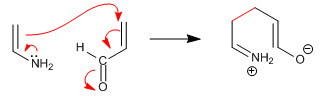
Stage 1. Nucleophilic attack of the enamine on the a,b-unsaturated
Stage 2. Acid-base balance
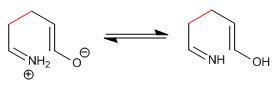
Stage 3. Keto-enol tautomerism
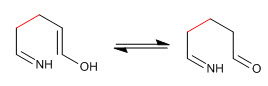
Stage 4. Imine-enamine tautomerism
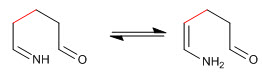
Step 5. Cyclization by nucleophilic addition of the amino to the carbonyl
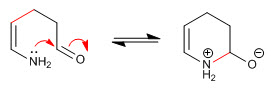
Stage 6. Acid-base balance
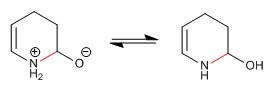
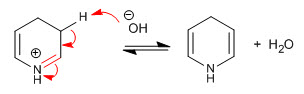
Step 7. Elimination of the hydroxyl
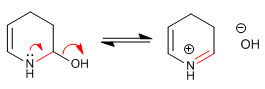
Stage 8. Elimination