PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 15161
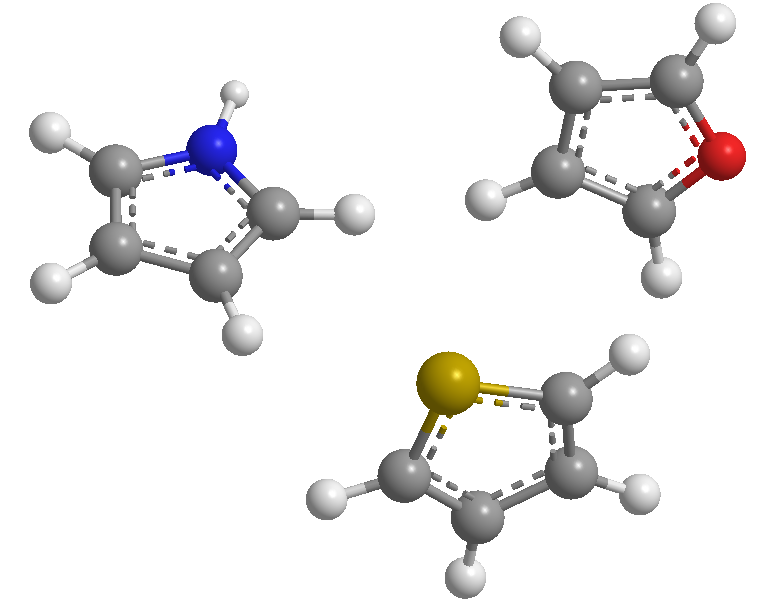
These are 5-membered heterocycles whose heteroatoms are nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. They are aromatic systems (they comply with Hückel's rule), with thiophene being the one with the highest stabilization energy (more aromatic), followed by pyrrole, with furan being the least aromatic due to the strong electronegativity of oxygen that makes delocalization of oxygen difficult. the electronic cloud.
pyrrole
thiophene
furan
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 24512
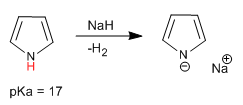
Pyrrole has an acid hydrogen on the nitrogen atom with pKa = 17. In the case of thiophene and furan, the acid hydrogens are located in position 2, although they have a much lower acidity than pyrrole.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 15232
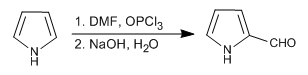
Of the three heterocycles studied in this topic, pyrrole is the most reactive in electrophilic substitution. In acid media it polymerizes, nitra in the presence of nitric acid and acetic anhydride, sulfone with the pyridine-SO 3 complex, halogen in the presence of dilute halogen solutions at low temperature and gives the Vilsmeier and Mannich reactions.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 17386
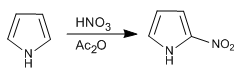
Pyrrole is nitrated with nitric in acetic anhydride since the sulfonitric mixture produces polymerization.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 16729
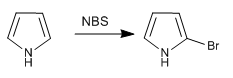
a) Halogenation of pyrrole
To avoid polyhalogenation, work with diluted halogen and at a low temperature should be used. Another option is to use NBS or NCS.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 21508
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 15829
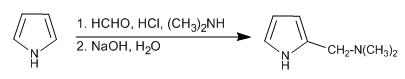
The Mannich reaction allows placing the aminomethyl group on position 2 of the pyrrole.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 12140
It is possible to add electrophiles to the 3,4 position of the pyrrole by placing bulky groups on the nitrogen atom, so that the 2,5 positions are prevented. One of the most used groups is triisopropylsilyl.
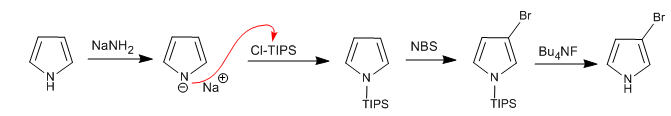
Read more: Electrophilic substitution at position 3 of pyrrole using Cl-TIPS
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 15128
Furan nitra with nitric acid in acetic anhydride, however, due to its poor aromaticity, is attacked by nucleophiles in the medium at its 5-position and requires a final stage of basic treatment or heating to restore aromaticity.
Stage 1. Generation of the electrophyte
![]()
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of furan on nitronium acetate
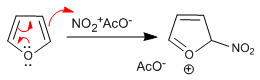
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 13970
Although it is less reactive than pyrrole in S E , it still has problems with polyhalogenations, so it is required to use dilute halogens and at low temperatures. NBS and NCS can also be used.
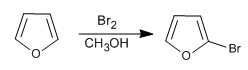
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 3981
a) Sulfonation of furan:
The furan sulfones with the SO 3 -Py complex
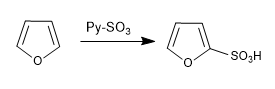
d) Vilsmeier formulation
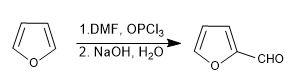
Read more: Sulfonation, formylation, Mannich and acetylation of furan
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 6004
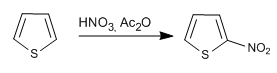
The reagents and reaction conditions are similar to those used in pyrrole.
a) Nitration of thiophene
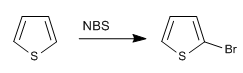
b) Halogenation of thiophene
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 2621
Pyrrole, thiophene and furan are not attacked by nucleophiles due to the strong electron density of the ring (excent p systems). Therefore, nucleophilic addition reactions, characteristic of p- deficient systems such as pyridine, quinoline and isoquinoline, are not observed.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 9914
The inability to stabilize the intermediate formed after nucleophilic attack makes this reaction impossible in 5-membered heterocycles. However, the presence of deactivating groups attached to the ring can make up for this deficiency, allowing the reaction.
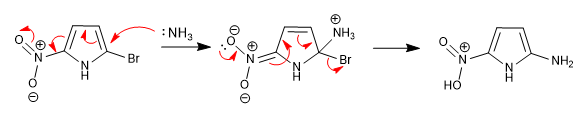
The nitro located in position 5 allows the delocalization of the charge generated during the addition stage.
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 4770
The reaction of halogenated heterocycles with lithium organometallics produces the exchange of halogen for the metal, generating a new organometallic that allows attacking a wide variety of electrophiles.
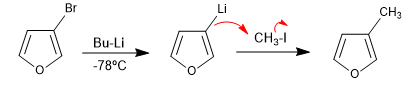
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 3569
The low aromaticity of furan allows it to participate in reactions that destroy the conjugation of the ring, such as: Diels-Alder, 1,3-dipolar, photochemical and kelotropic.
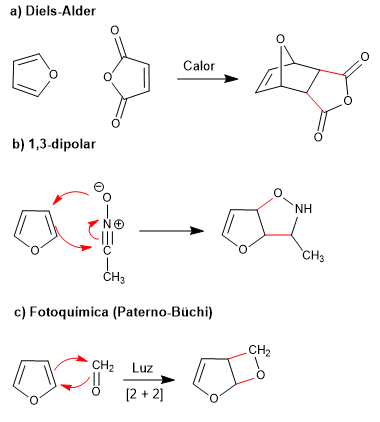
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 2676
a) Leaving group near the ring
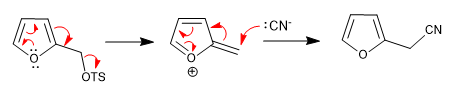
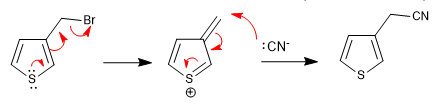
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 1950
Furan opens in aqueous acid media to form 1,4-dicarbonyls. The reaction follows the reverse steps of the Paal-Knorr synthesis.
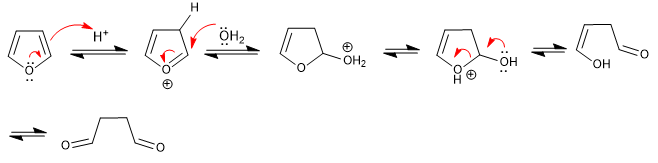
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 4610
Generates pyrroles by reaction of 1,4-dicarbonyls with amines or ammonia.
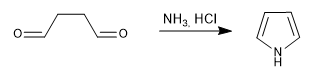
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 4256
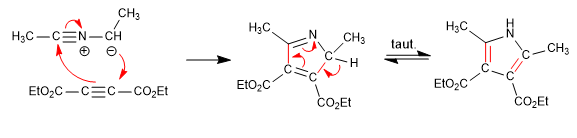
It consists of the reaction of a primary amine with a 3-ketoester forming an imine, which later tautomerizes to enamnin, attacking an a-haloketone. In a subsequent cyclization stage, pyrrole is obtained.
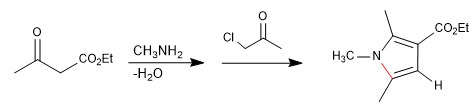
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- PYRROL, THIOPHENE AND FURAN THEORY
- Hits: 2345
Nitrile ylides react with alkynes, via the 1,3-dipolar reaction, to generate pyrroles