The condensation of two molecules of ethanal and one of methane produces a 1,5-dicarbonyl compound that reacts with ammonia to generate pyridine.
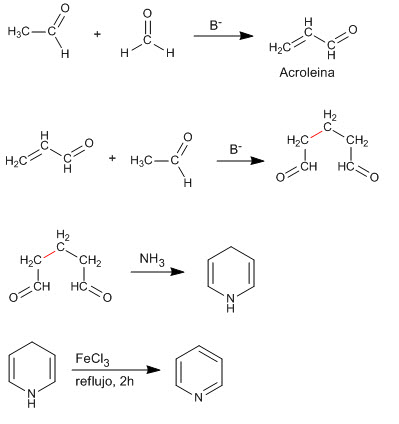
The first stage consists of the aldol condensation of methanal with ethanal, to form acrolein. In the second stage, the Michael addition between acrolein and a second equivalent of ethanal occurs, to yield a α , β -unsaturated.
The final condensation of the ammonia with the α , β -unsaturated produces, after an oxidation step, the final pyridine.