QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 4031
a) Basicity
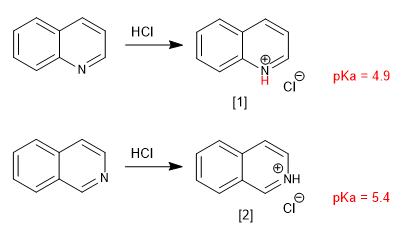
Quinoline and isoquinoline behave like bases through the lone pair of nitrogen. In acid media they are protonated to form quinolinium and isoquinolinium salts.
quinolinium salt
isoquinolinium salt
Substituents modify basicity in a manner analogous to pyridine. Donor groups increase the basicity and attractor groups decrease it.
Read more: Reactions with nitrogen lone pair: quinoline and isoquinoline
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 18538
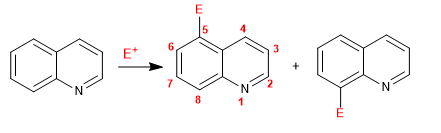
Quinoline and isoquinoline react with electrophiles through the benzene ring (carbocycle), due to its higher electronic richness, compared to the pyridine ring. The most favored positions are 5 and 8.
Read more: Electrophilic substitution reaction in quinoline and isoquinoline
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 3128
N-oxides allow electrophiles to be placed at position 4 of the quinoline.
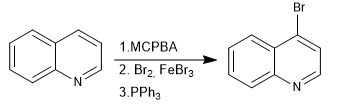
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 3062
The reaction between halogenated derivatives of quinoline and isoquinoline with organolithics at low temperature produces the exchange of halogen for the metal, generating new organolithics on the ring.
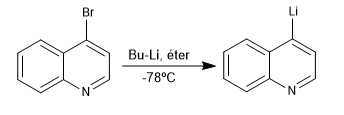
Read more: Lithiation reaction in quinoline and isoquinoline
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 4841
The nucleophiles add to carbon 2 of the quinoline, although under certain conditions it can also receive attacks on its carbon 4.
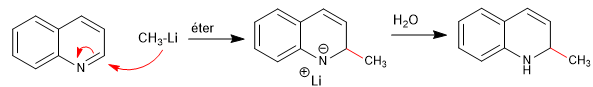
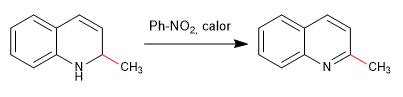
Read more: Nucleophilic addition to quinolines and isoquinolines
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 11098
Halogenated quinolines in position 2,4 very easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. For its part, isoquinoline can only give this reaction in position 1. All nucleophiles with the capacity to give S N 2 can participate in this reaction, bad nucleophiles such as water or alcohols require heat input.
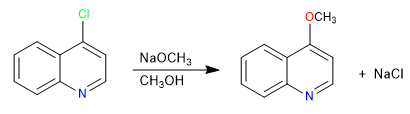
Read more: Nucleophilic substitution in quinoline and isoquinoline
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 2450
Pyridines with 2,4-position alkyl groups have acidic hydrogens on the carbon adjacent to the pyridine ring.
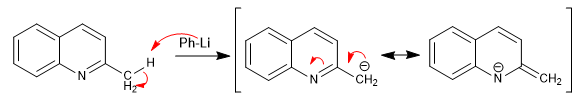
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 32065
In the Skraup synthesis, aniline reacts with a,b-unsaturated carbonyls in an acid medium to form 1,2-dihydroquinolines, which are transformed into quinolines by oxidation. The a,b-unsaturated carbonyl can be obtained by dehydration of 1,2,3-propanetrium.
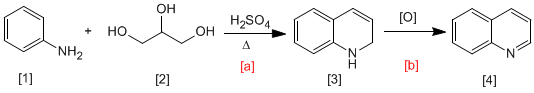
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 14701
In the Conrad-Limpach synthesis, quinolones are obtained by reacting aniline with 3-ketoesters. Under kinetic conditions the 4-quinolone is obtained and under thermodynamic conditions the 2-quinolone.
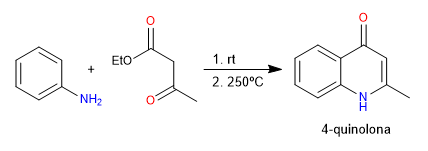
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 5354
In the Combes synthesis, quinolines are obtained by reacting aniline with 1,3-dicarbonyls, in the presence of acid catalysis. In a first stage, the imine is formed, which tautomerizes to enamin,a, activating the aromatic ring by giving up the nitrogen pair. In the last stage, cyclization occurs by attack of benzene to the carbonyl of the chain
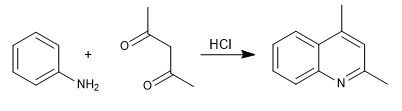
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 7119
The Friedländer synthesis prepares quinolines from an ortho-acetylated nitrobenzene and a ketone. The synthesis begins with an aldol condensation in a basic medium. Reduction of the nitro group to amino allows cyclization by imine formation.
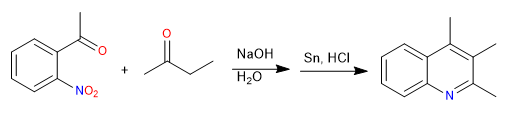
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 3533
The reaction between 2-aminoethylbenzene and an alkanoyl halide in the presence of pyridine forms an amide. The amide is converted to the Vilsmeier electrophile by reaction with phosphorous oxytrichloride. The cyclization is produced by attack of the benzene to said electrophile. A final oxidation generates isoquinoline.
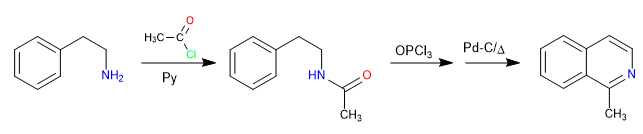
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 3530
Pictet Spengler is a Mannich type reaction. In the first stage, the Mannich electrophile is formed by reaction of the amine with an aldehyde in a hydrochloric acid medium. In the final stage, the cyclization takes place by attack of the benzene on the Mannich electrophile. The isoquinoline is obtained after a double oxidation.
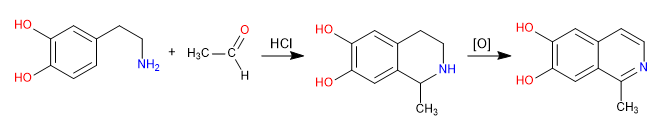
- Details
- Germán Fernández
- QUINOLINE AND ISOQUINOLINE THEORY
- Hits: 3954
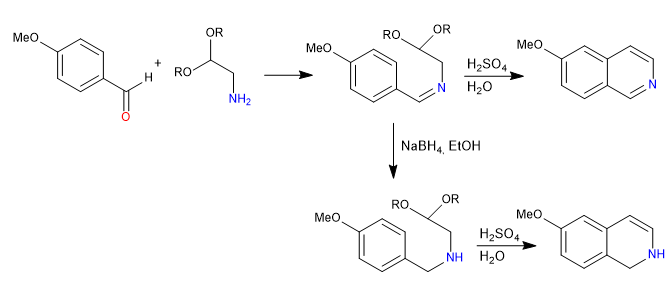
The Pomeranz-Fritsch synthesis prepares isoquinolines by reacting benzaldehydes with protected a-aminoaldehydes in the form of acetals. In a first stage, the imine is formed by reaction between benzaldehyde and the amine. In a second step, the acetal is broken with aqueous sulfuric acid, leaving the aldehyde free, which cyclizes under benzene attack.